Description
Expandable container homes are changing how housing is designed, manufactured, and delivered. Instead of long construction timelines, weather delays, and unpredictable costs, modular container solutions provide controlled production, rapid deployment, and consistent quality.
For homeowners, developers, and investors, expandable designs offer a practical way to create permanent or semi-permanent dwellings that can perform across coastal regions, remote sites, and growing urban areas.
This article explains how expandable container housing works, why demand is accelerating globally, and what engineering features determine long-term performance.
What Is an Expandable Container Home?
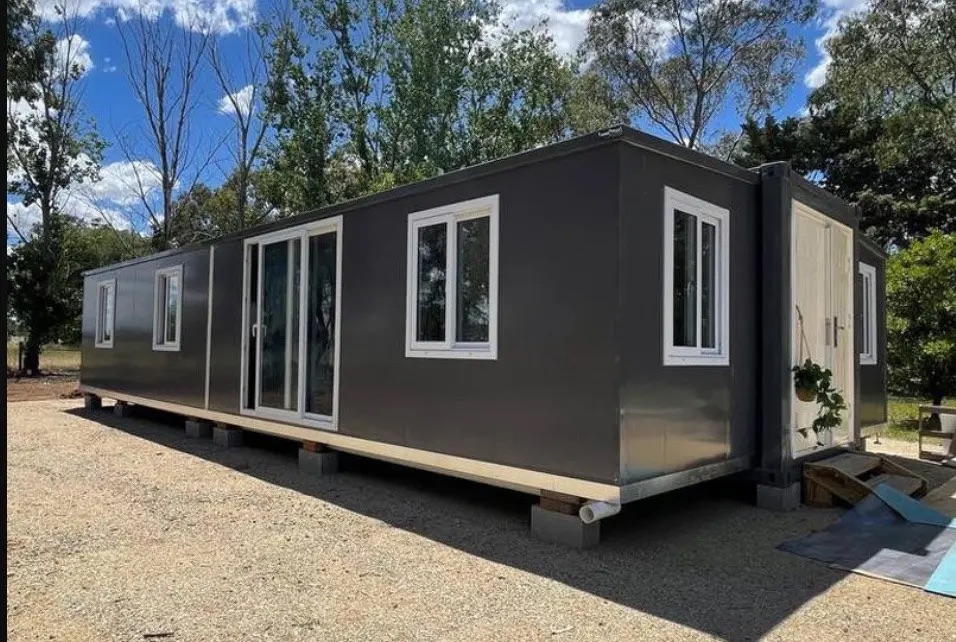
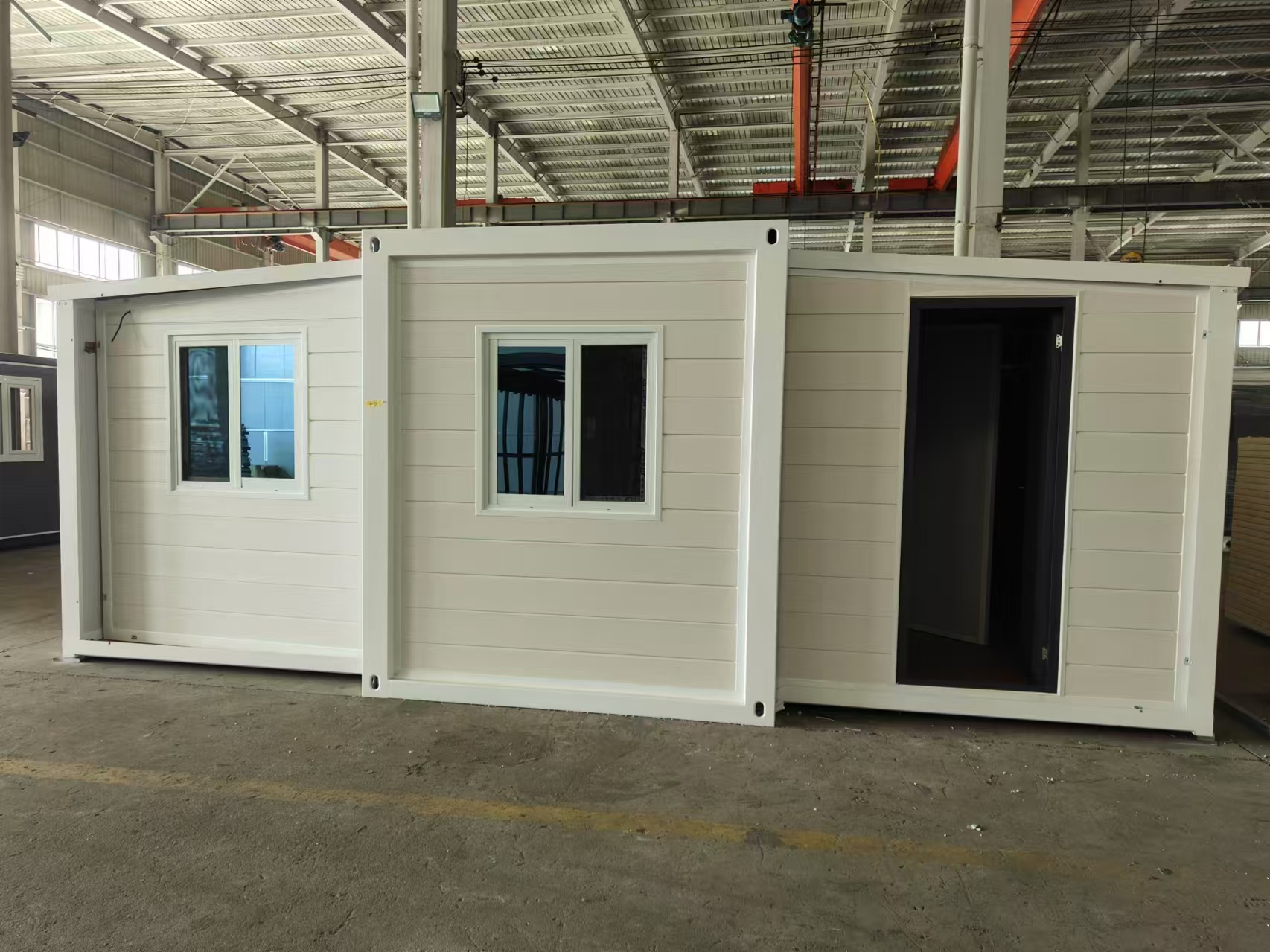
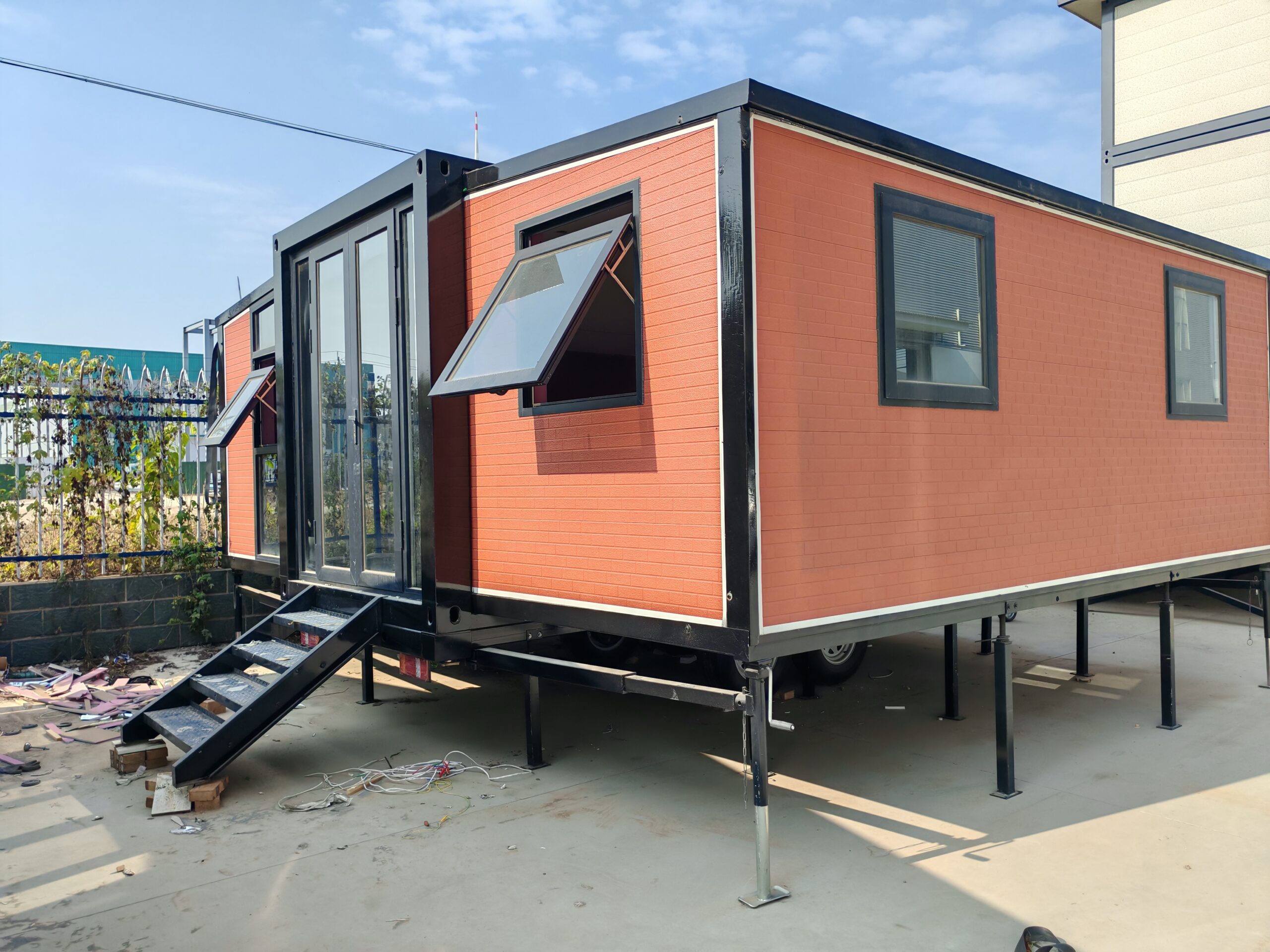
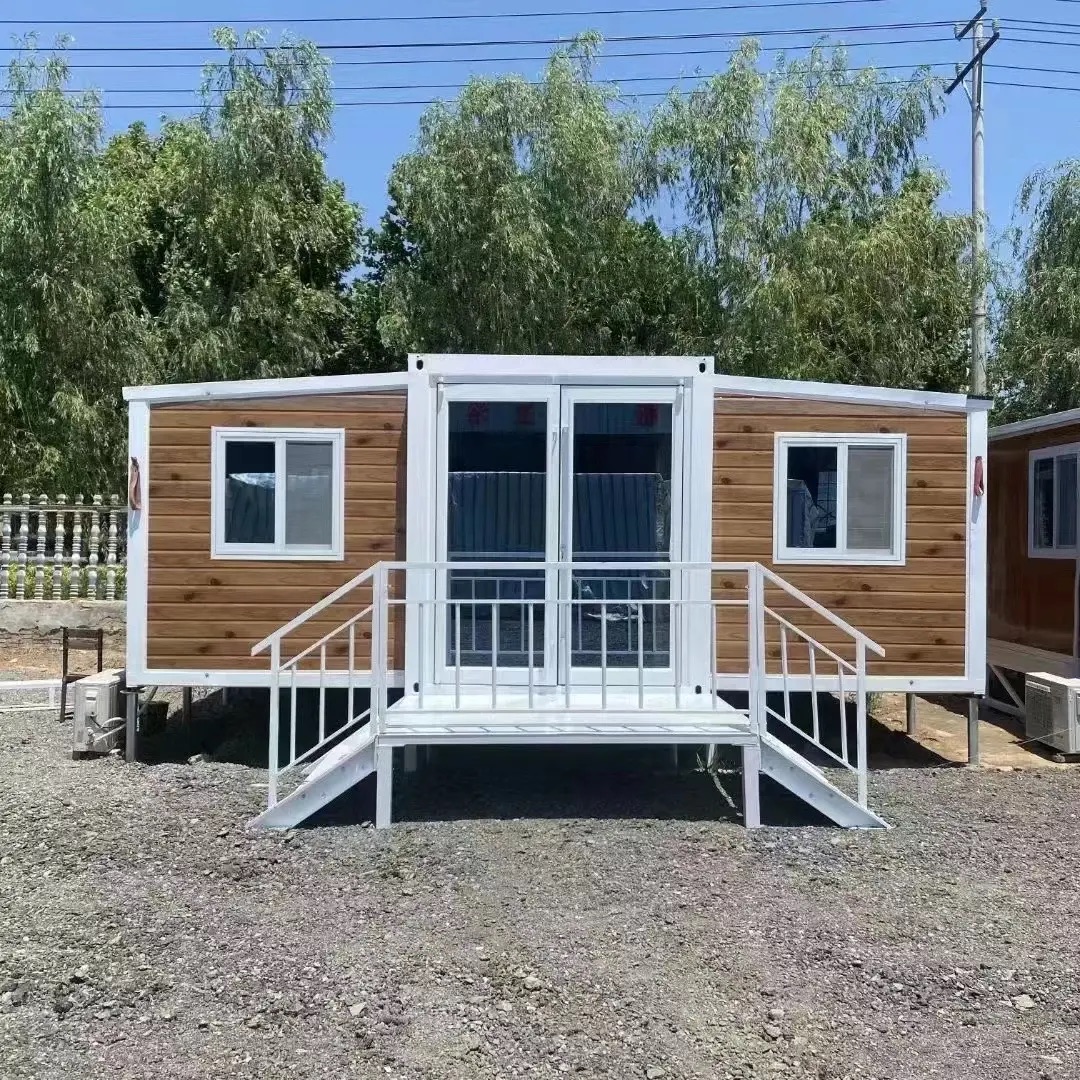
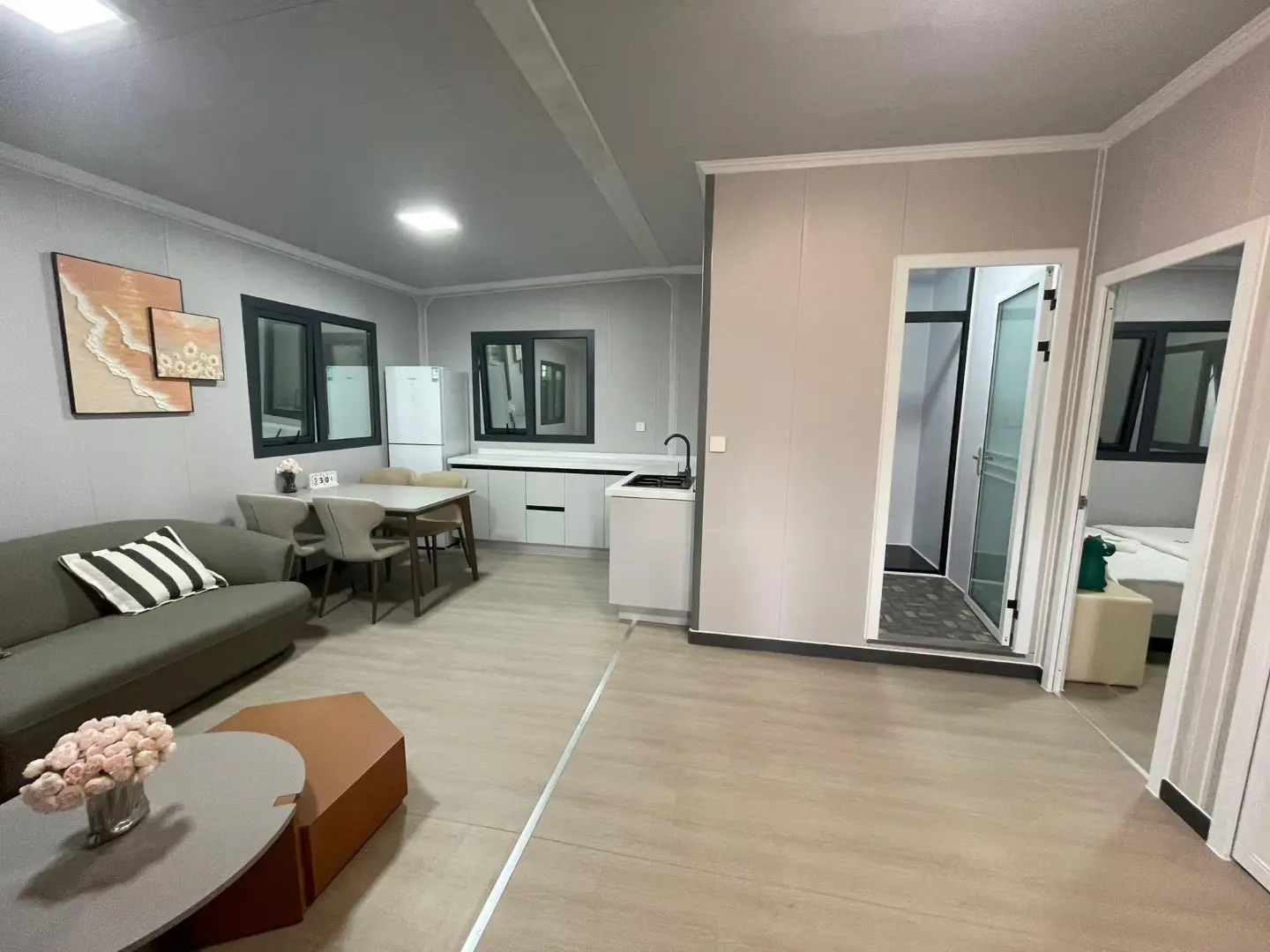
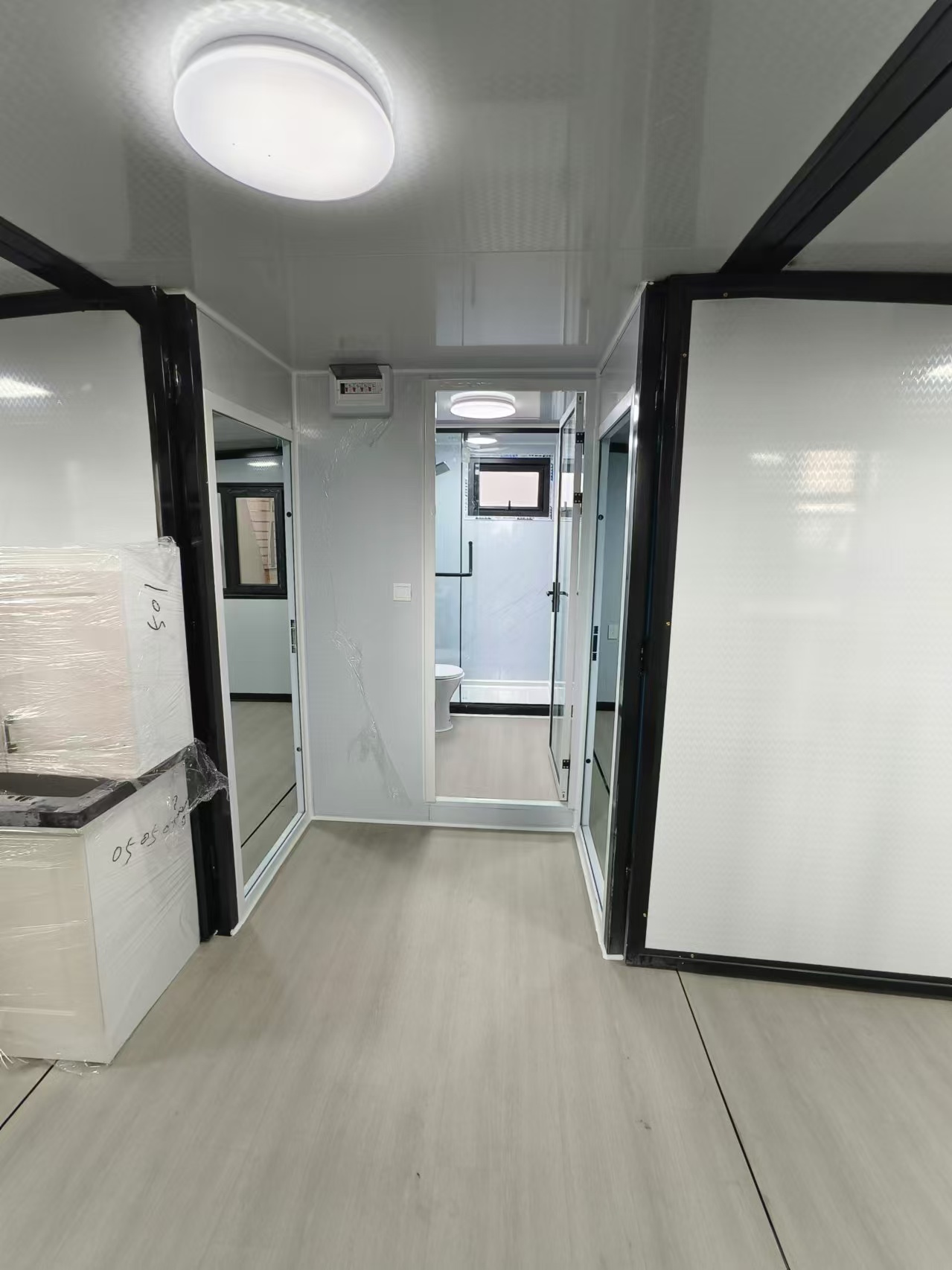
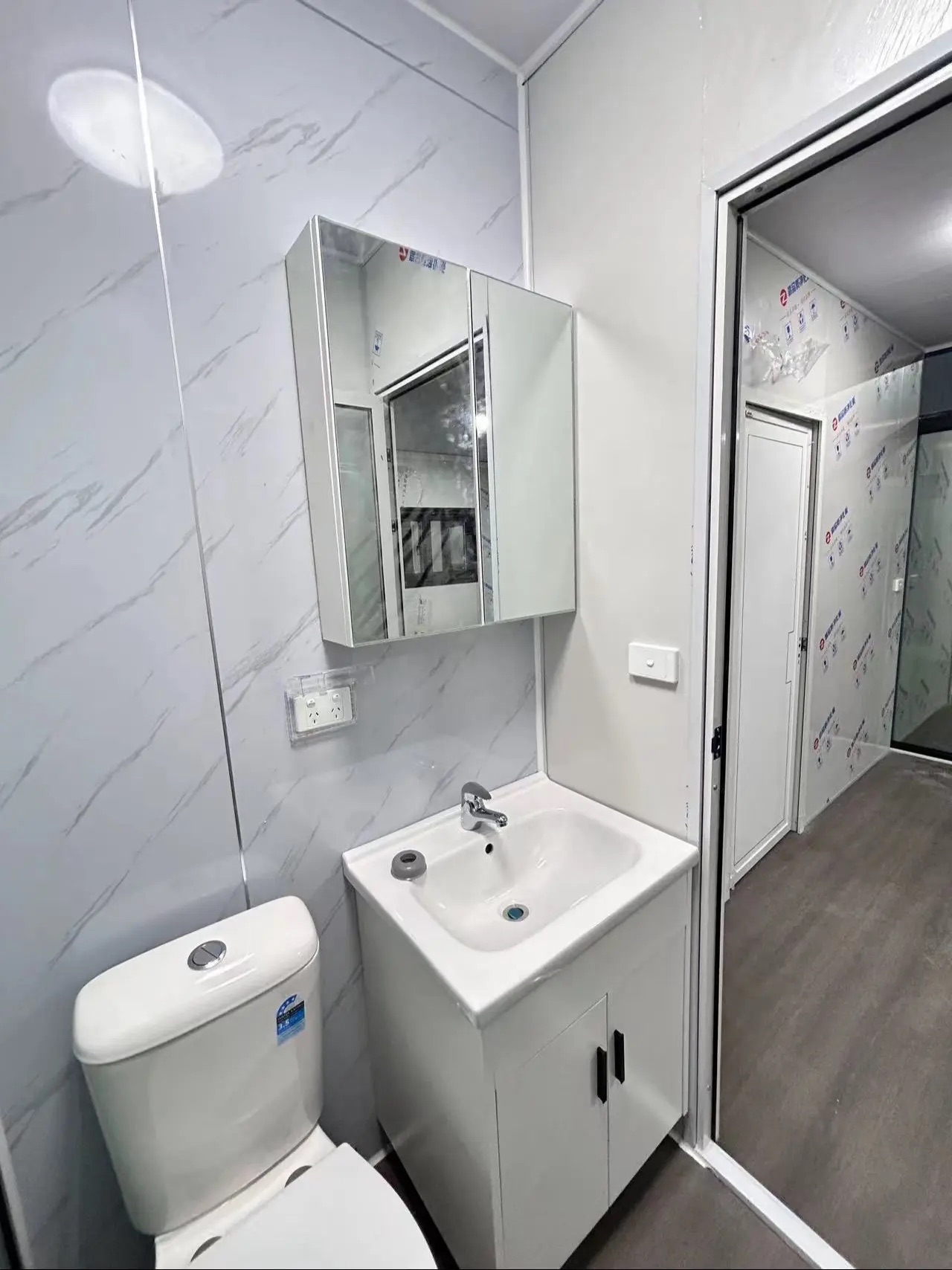
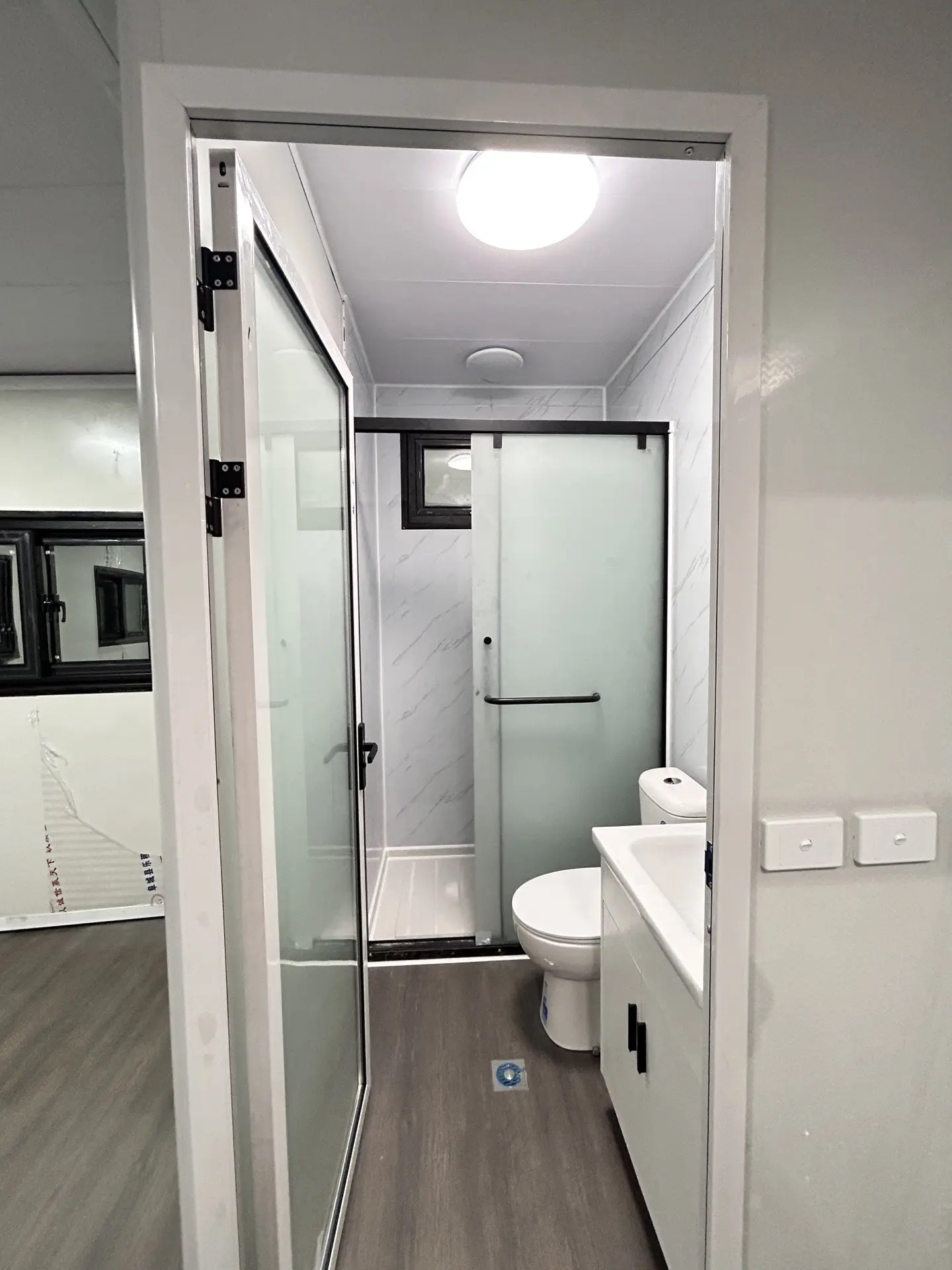
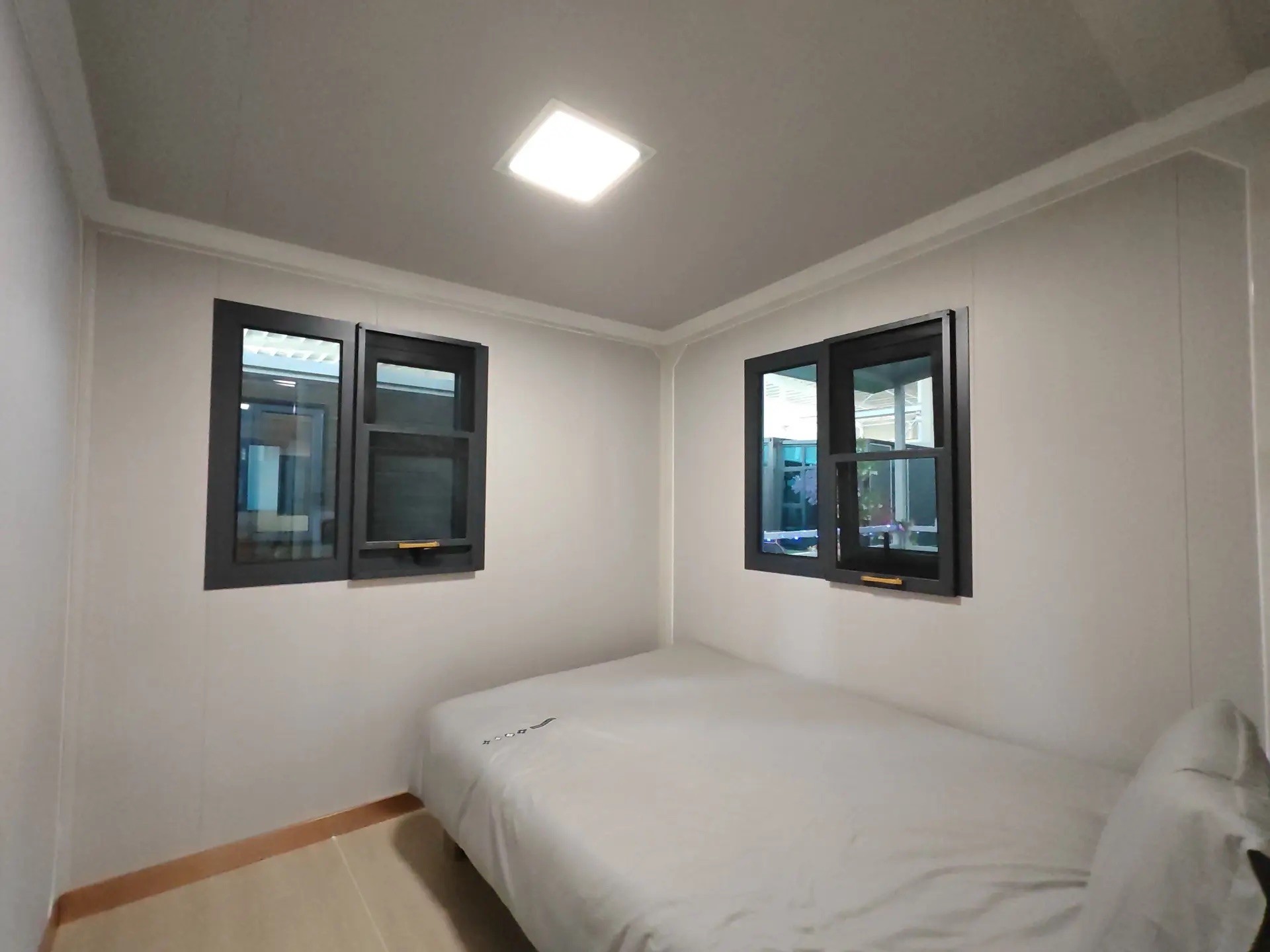
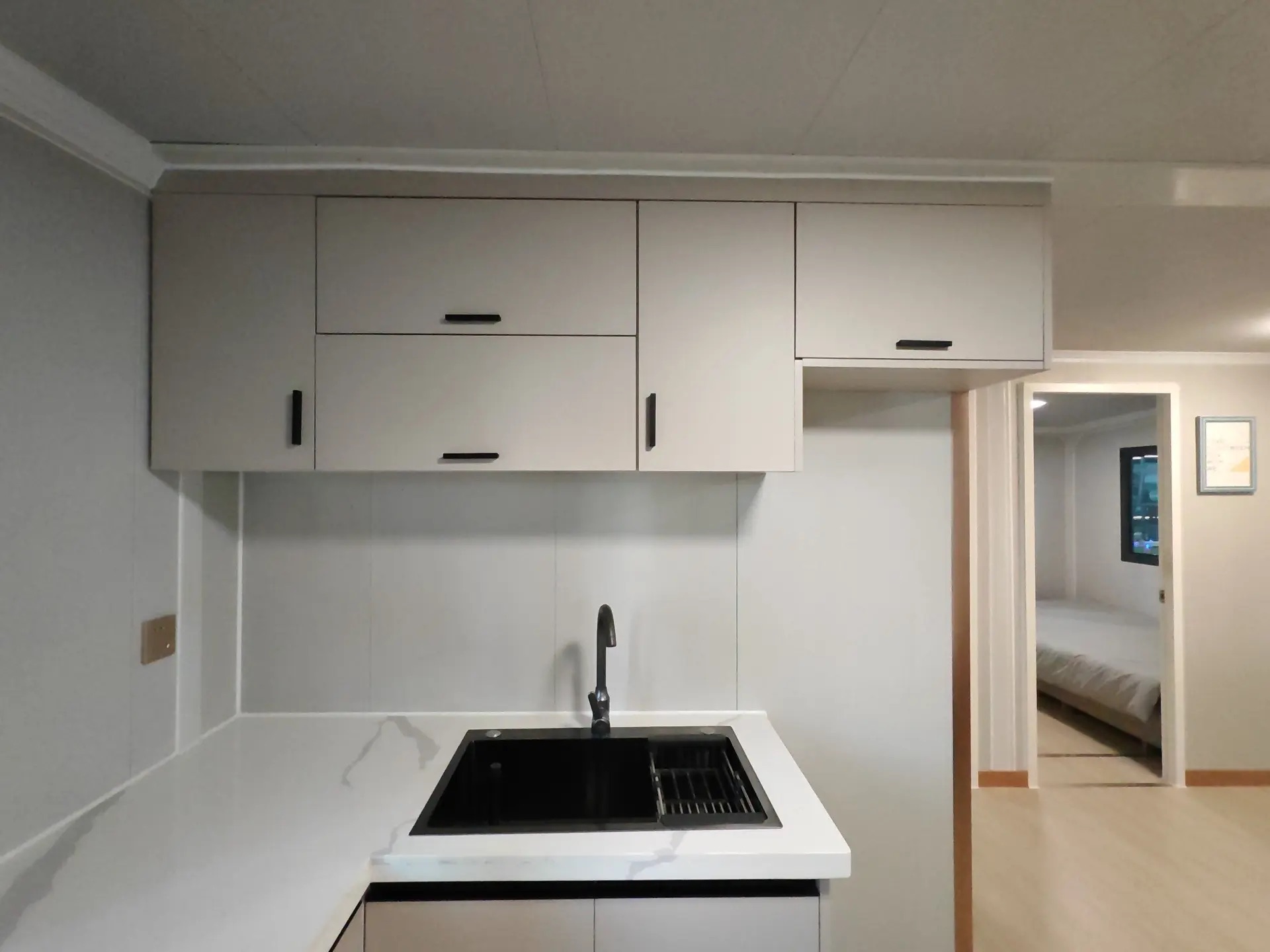
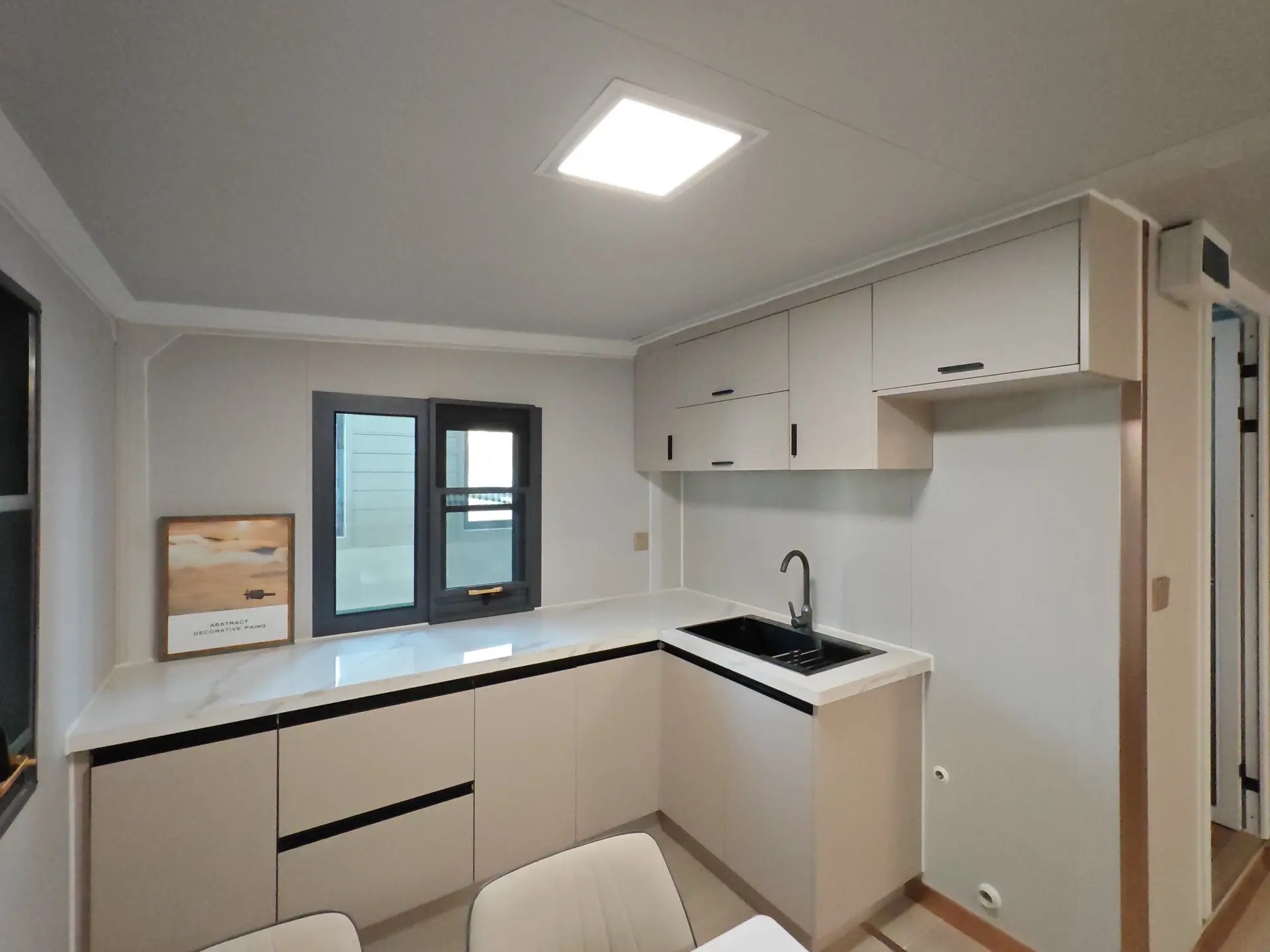
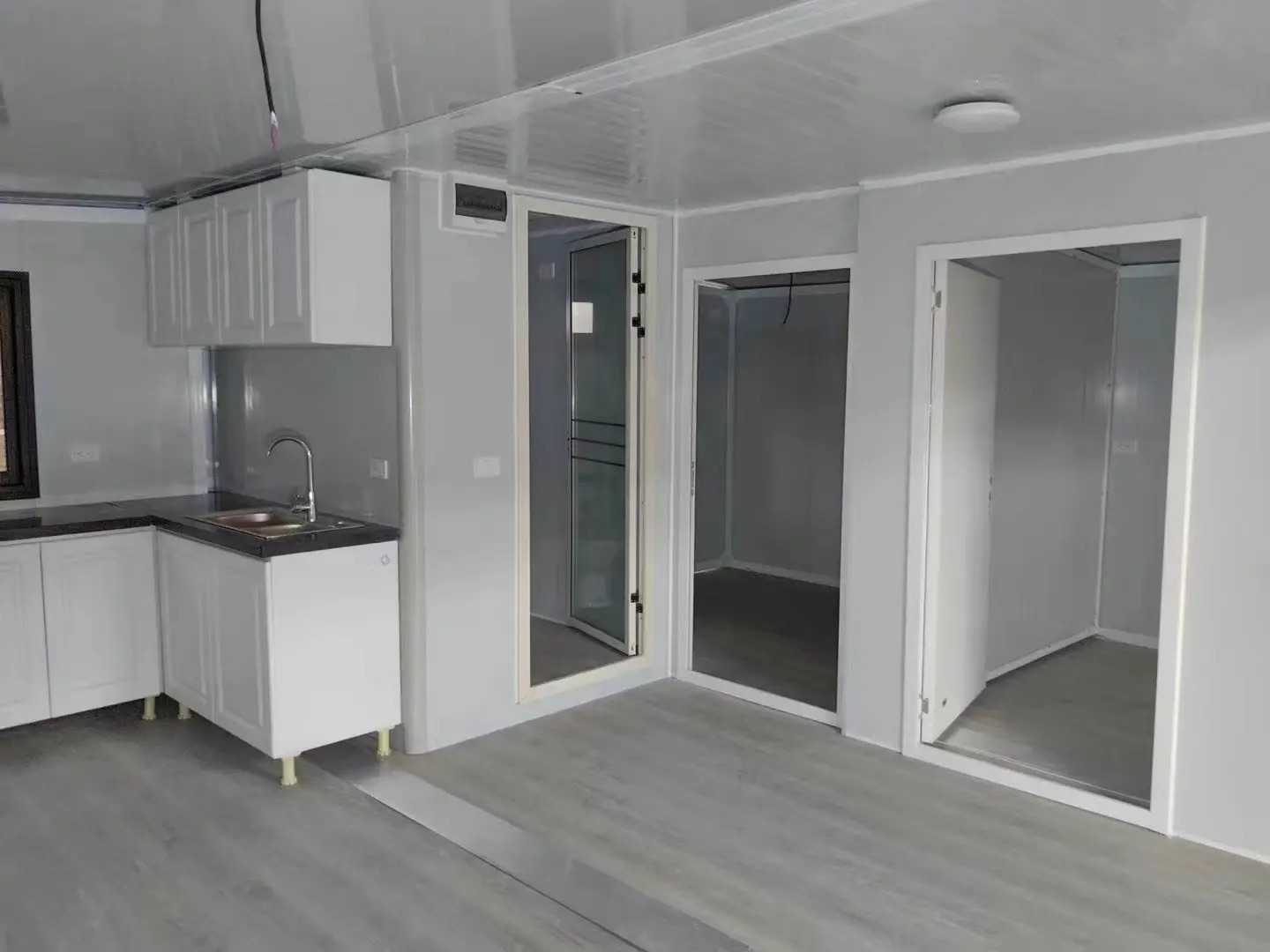
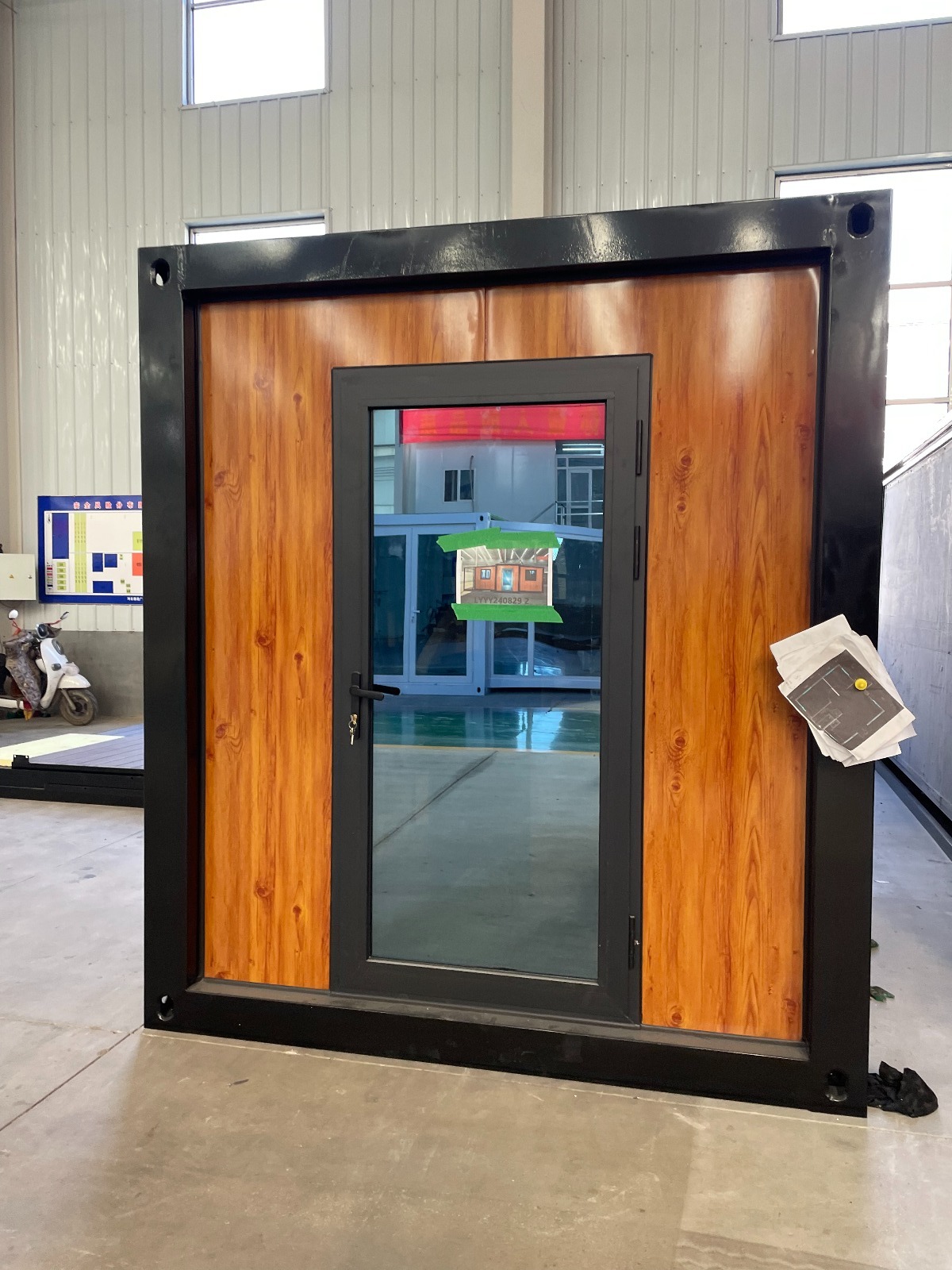
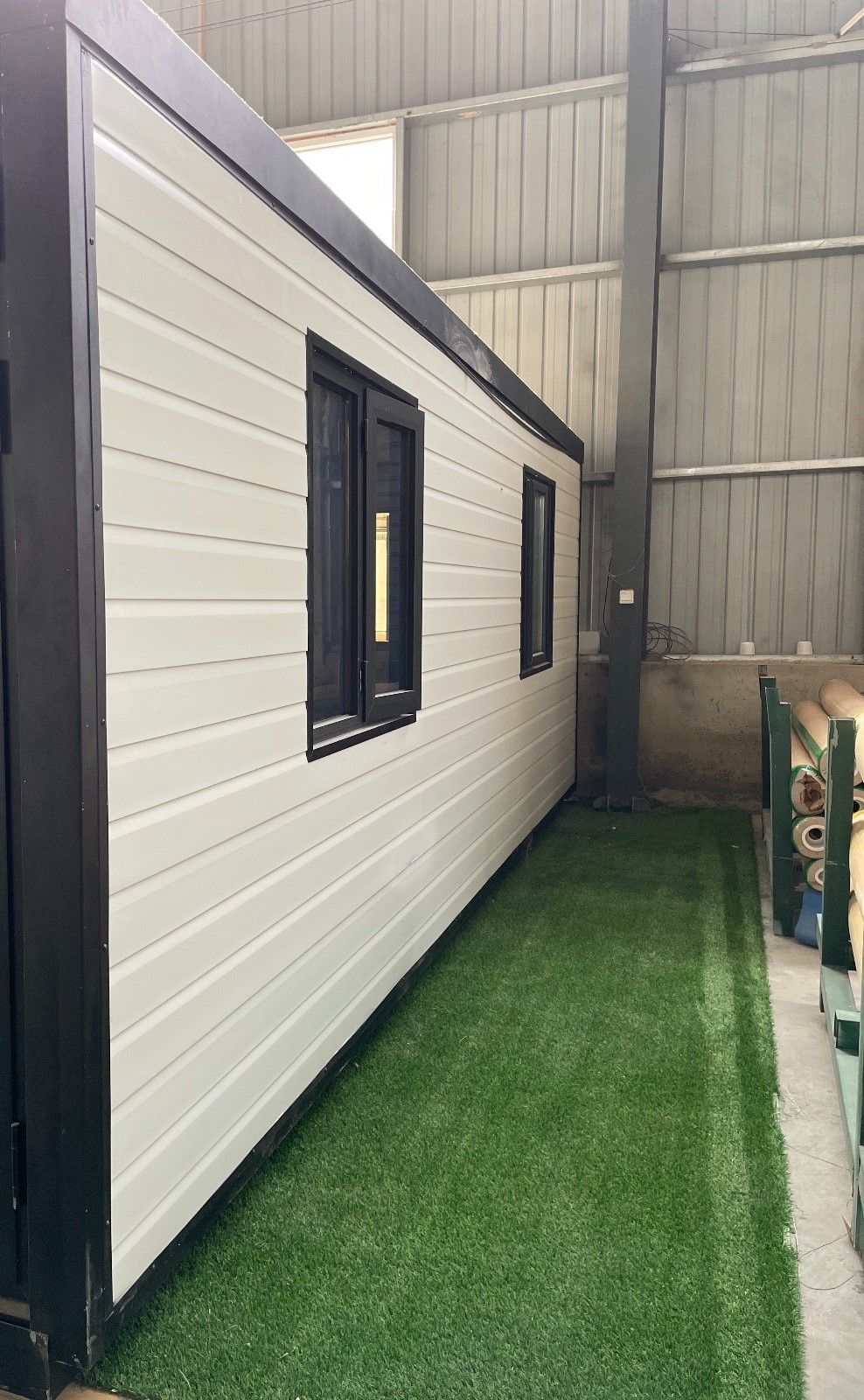
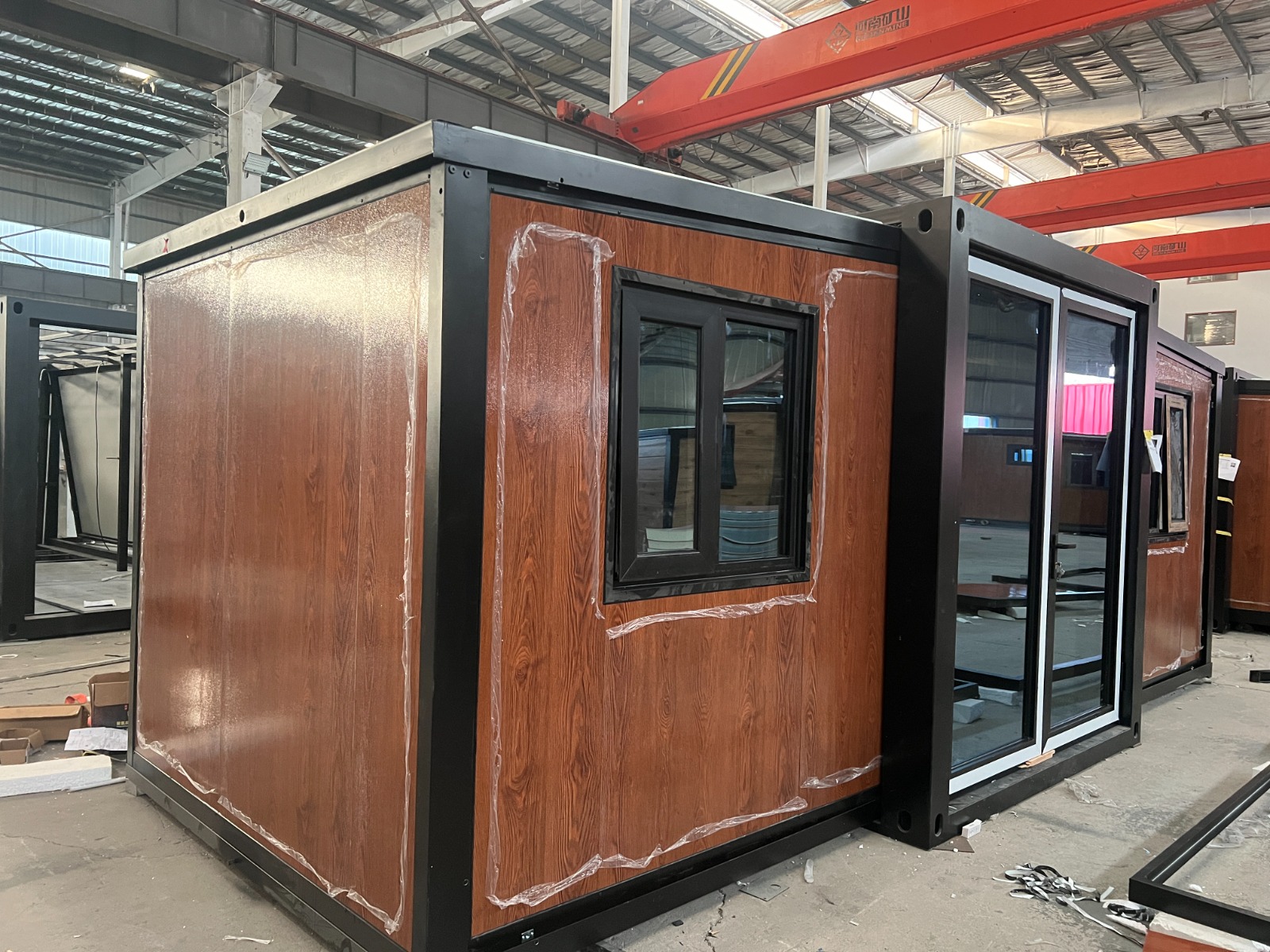
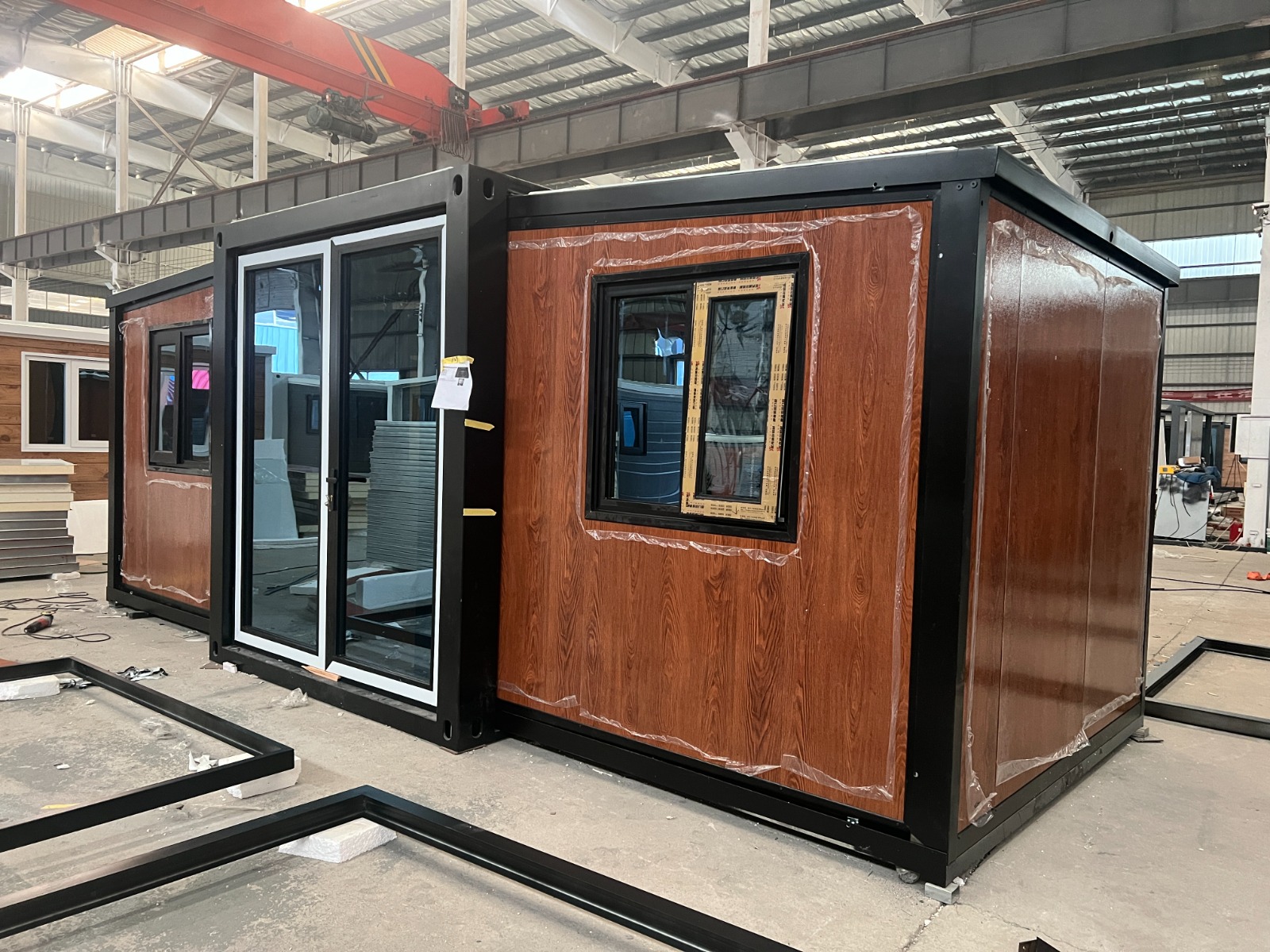
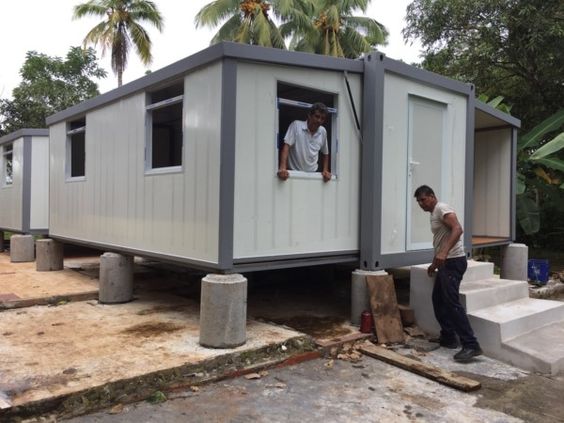
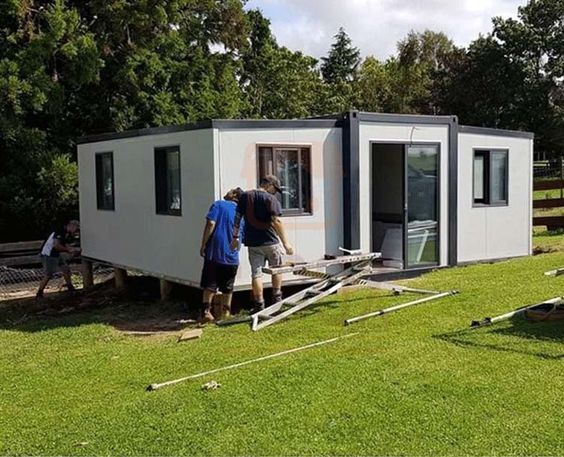
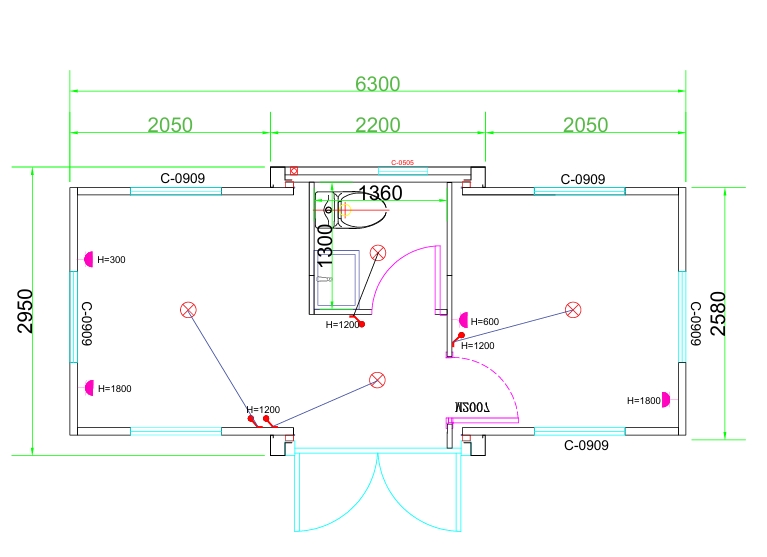
An expandable container home is a prefabricated dwelling built from a reinforced shipping-container structure that unfolds or extends once delivered to site.
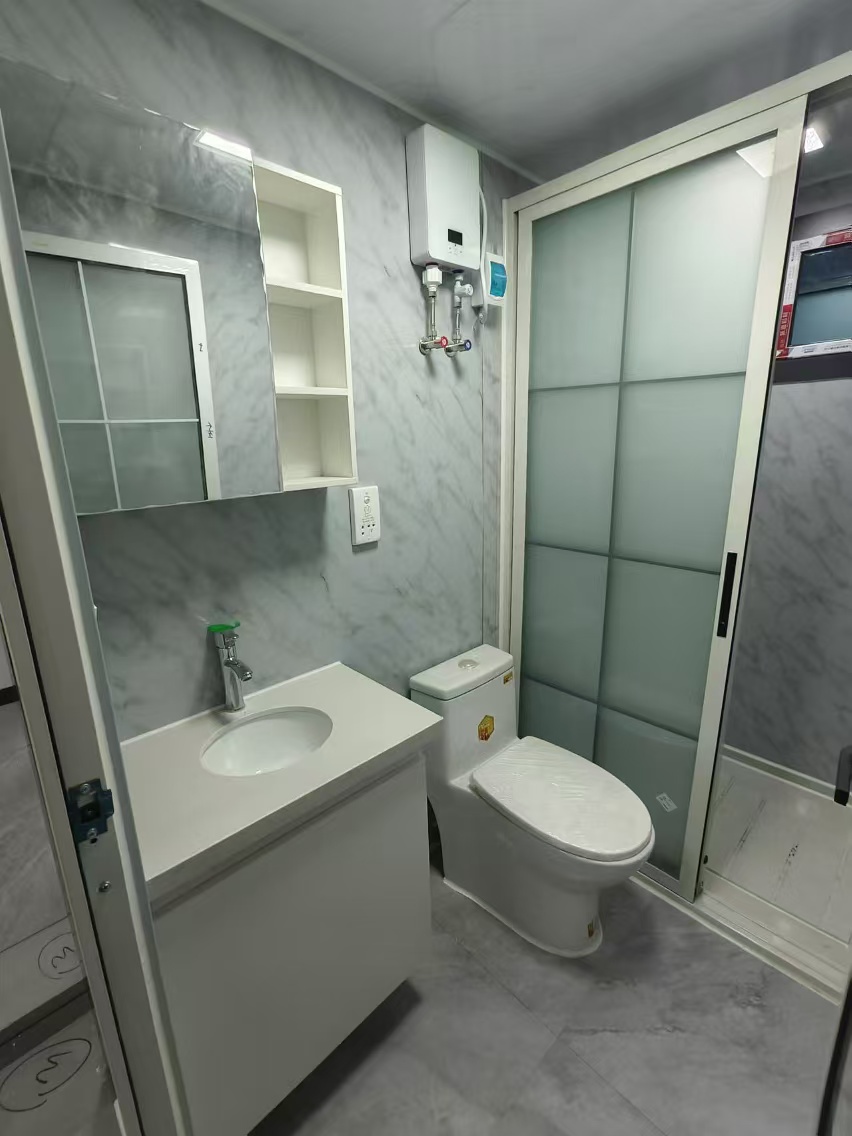
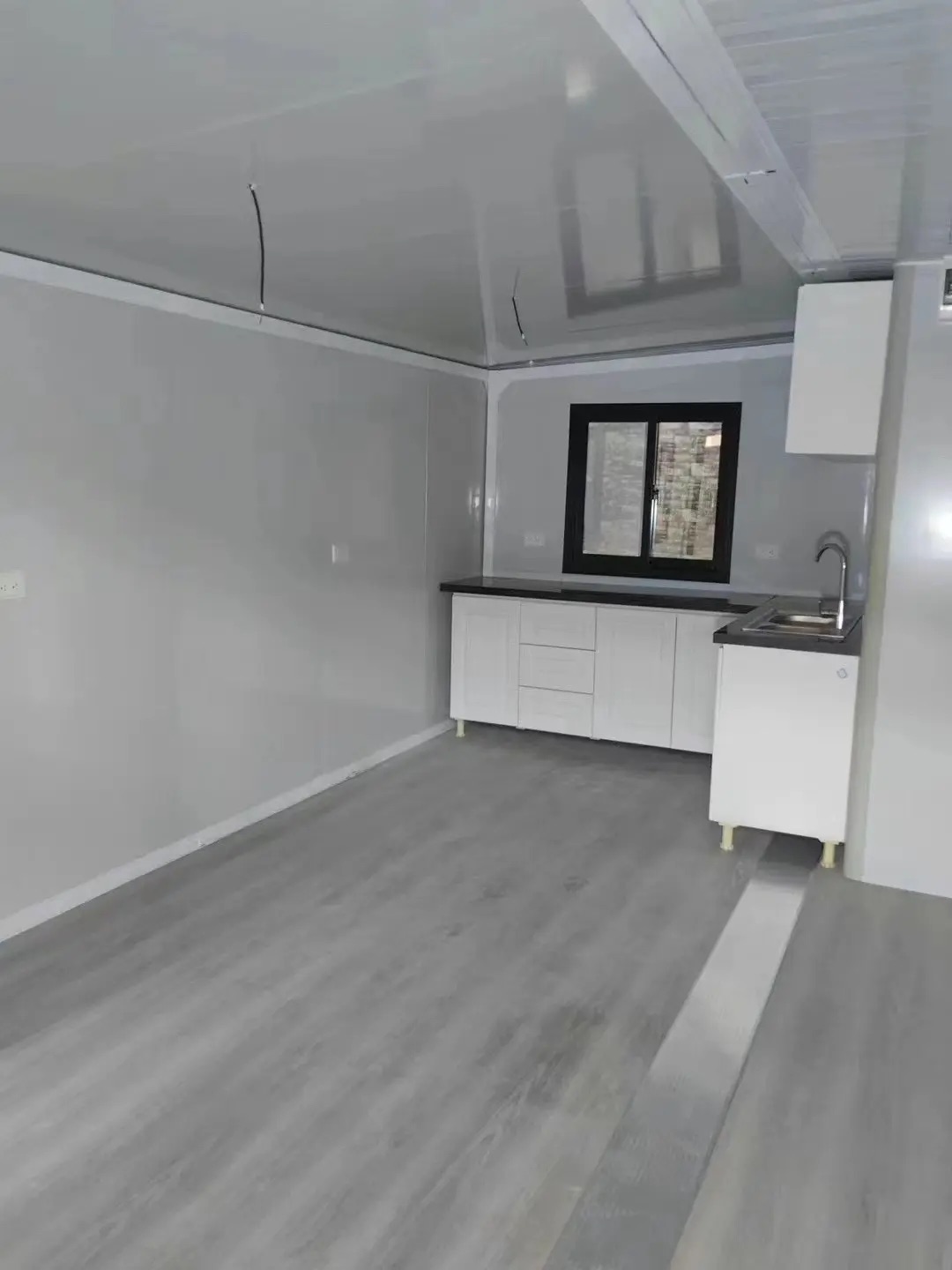
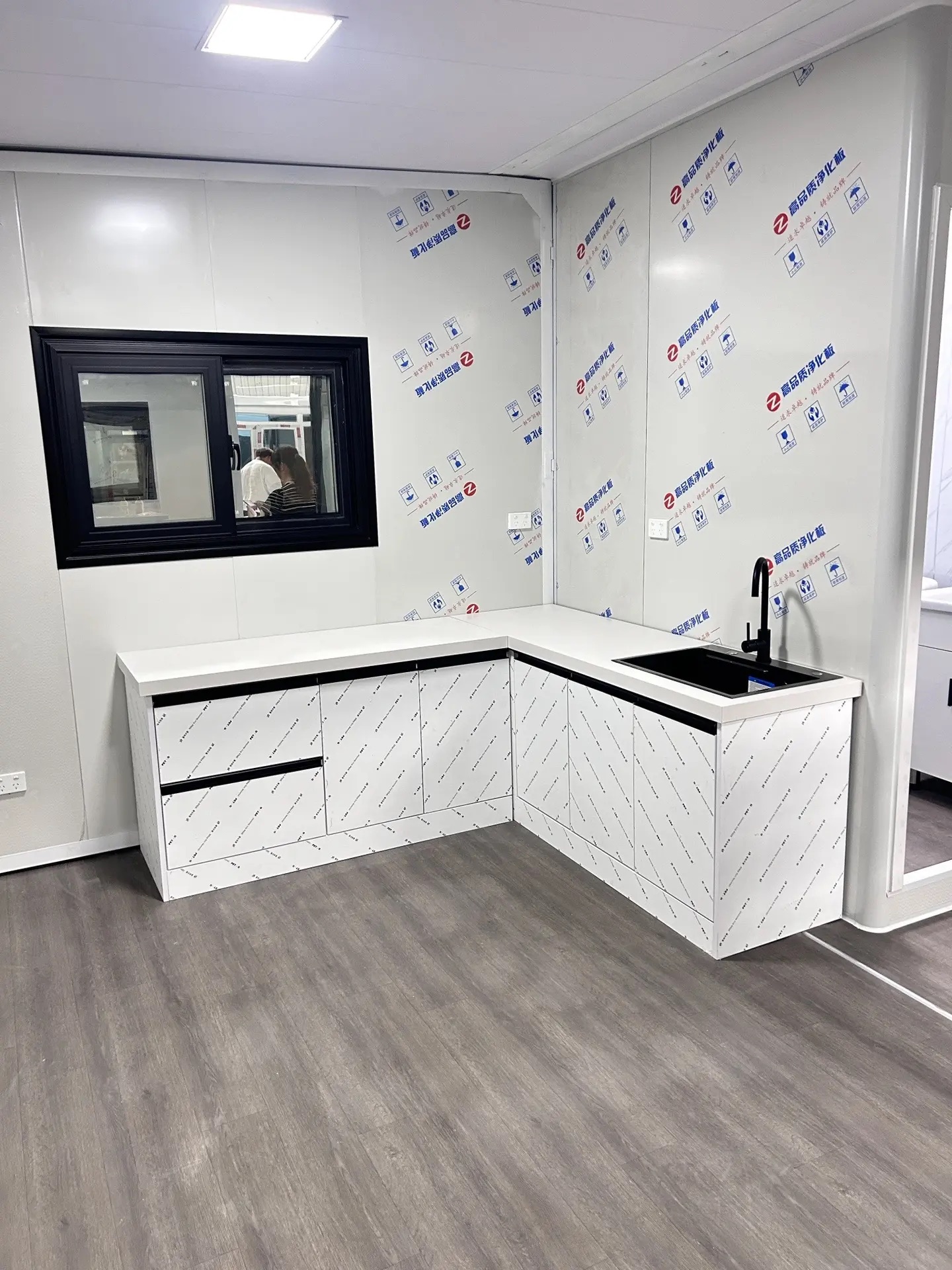
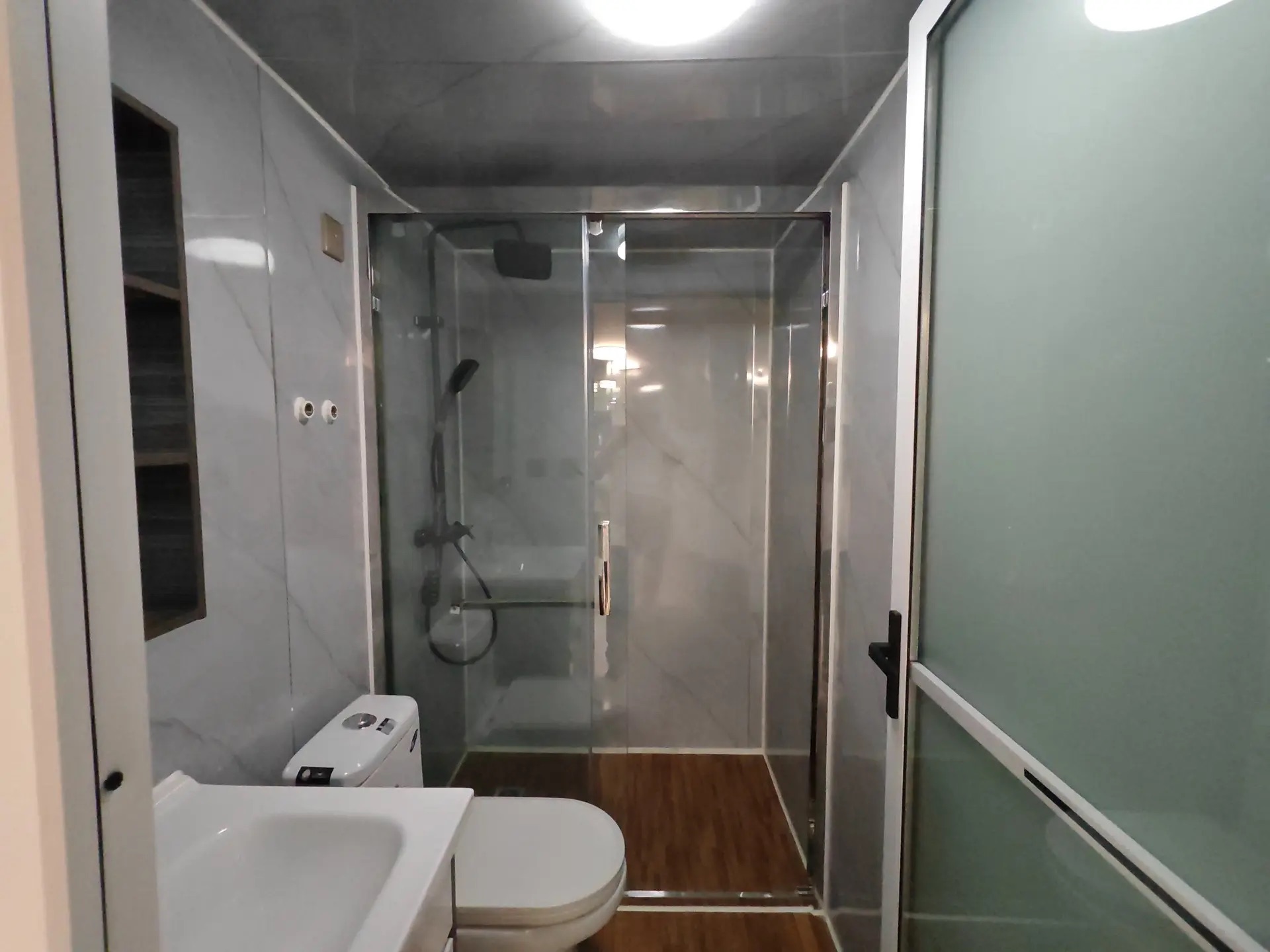
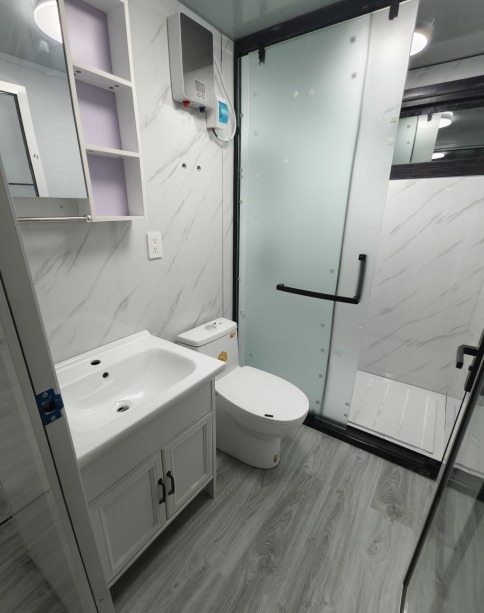
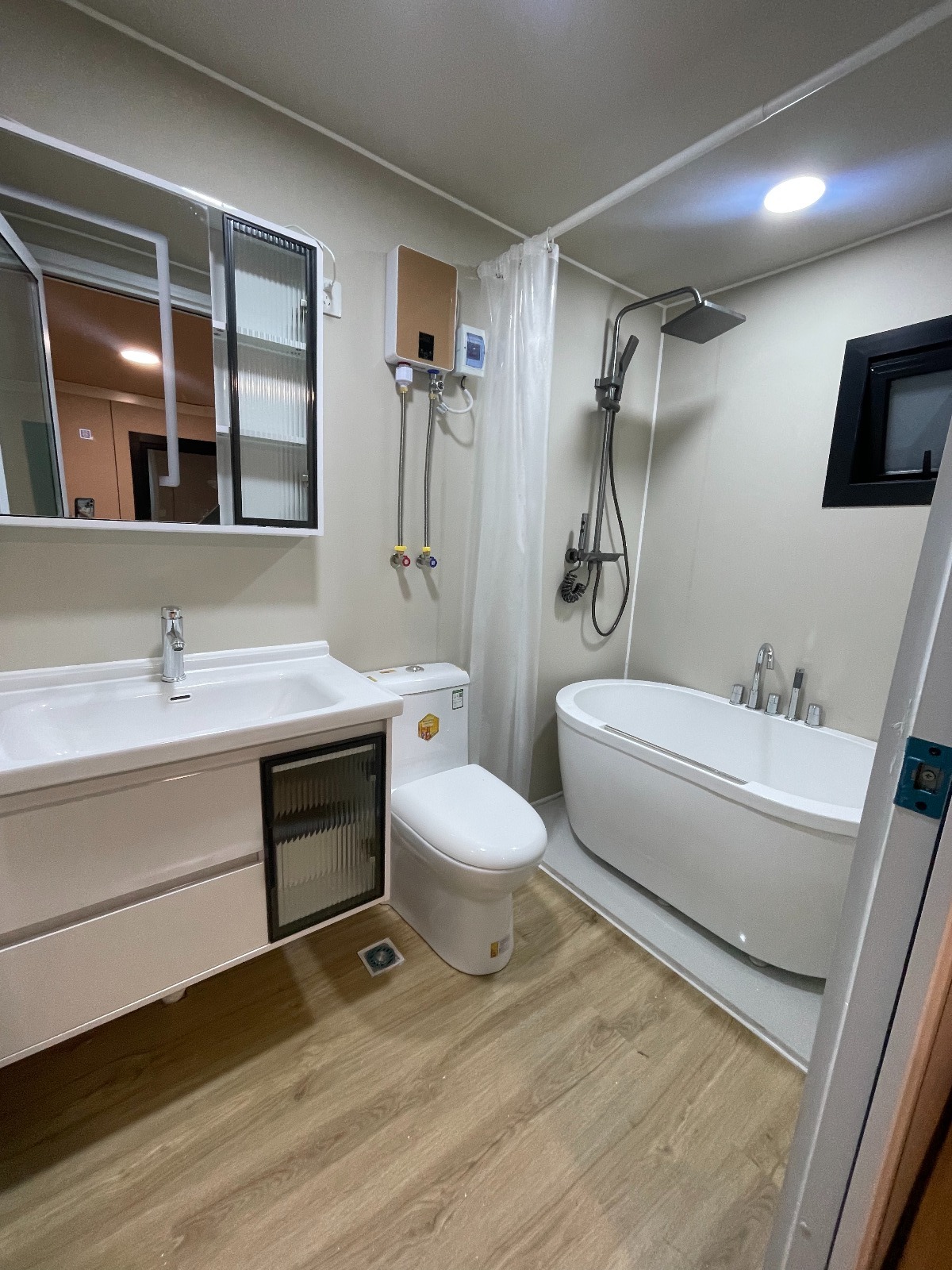
Unlike traditional builds, the majority of fabrication happens in a controlled factory environment. Plumbing, wiring, insulation, windows, and interior finishes are often pre-installed before transport.
Once on location, the home is positioned, expanded, connected to services, and can be operational within a very short timeframe.
Why Container Living Is Growing Rapidly
Affordability that remains predictable
Traditional construction is vulnerable to labour shortages, material cost fluctuations, and delays. Modular container housing reduces these variables through repeatable manufacturing and faster installation.
Durable structures and protective coatings also reduce lifecycle maintenance costs.
Speed of deployment
Many expandable homes can be ready for occupation within a day of delivery, depending on foundations and utility connections.
Sustainability advantages
Because they repurpose container structures and support solar, water capture, and off-grid systems, they align with environmentally focused developments and remote installations.
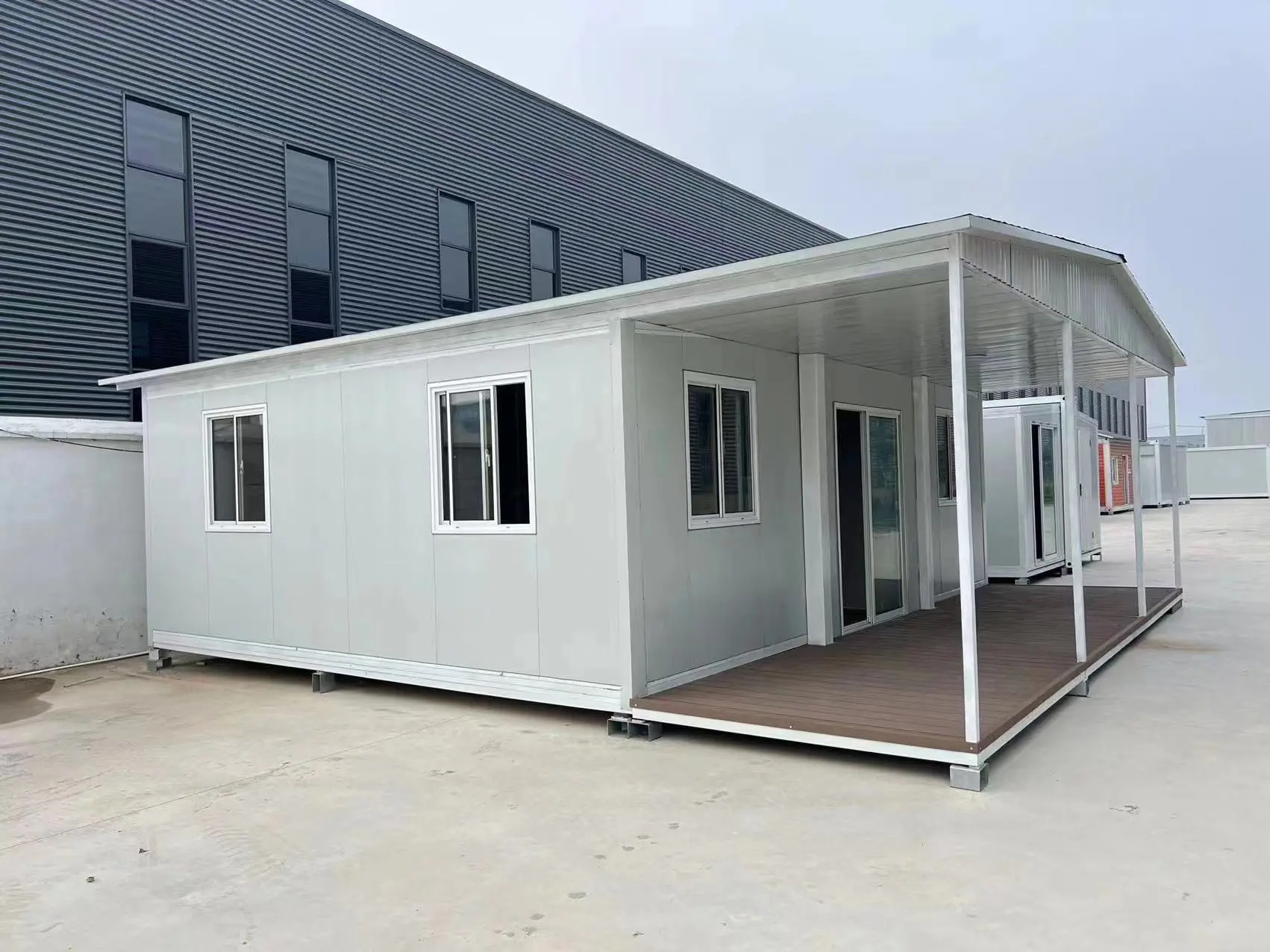
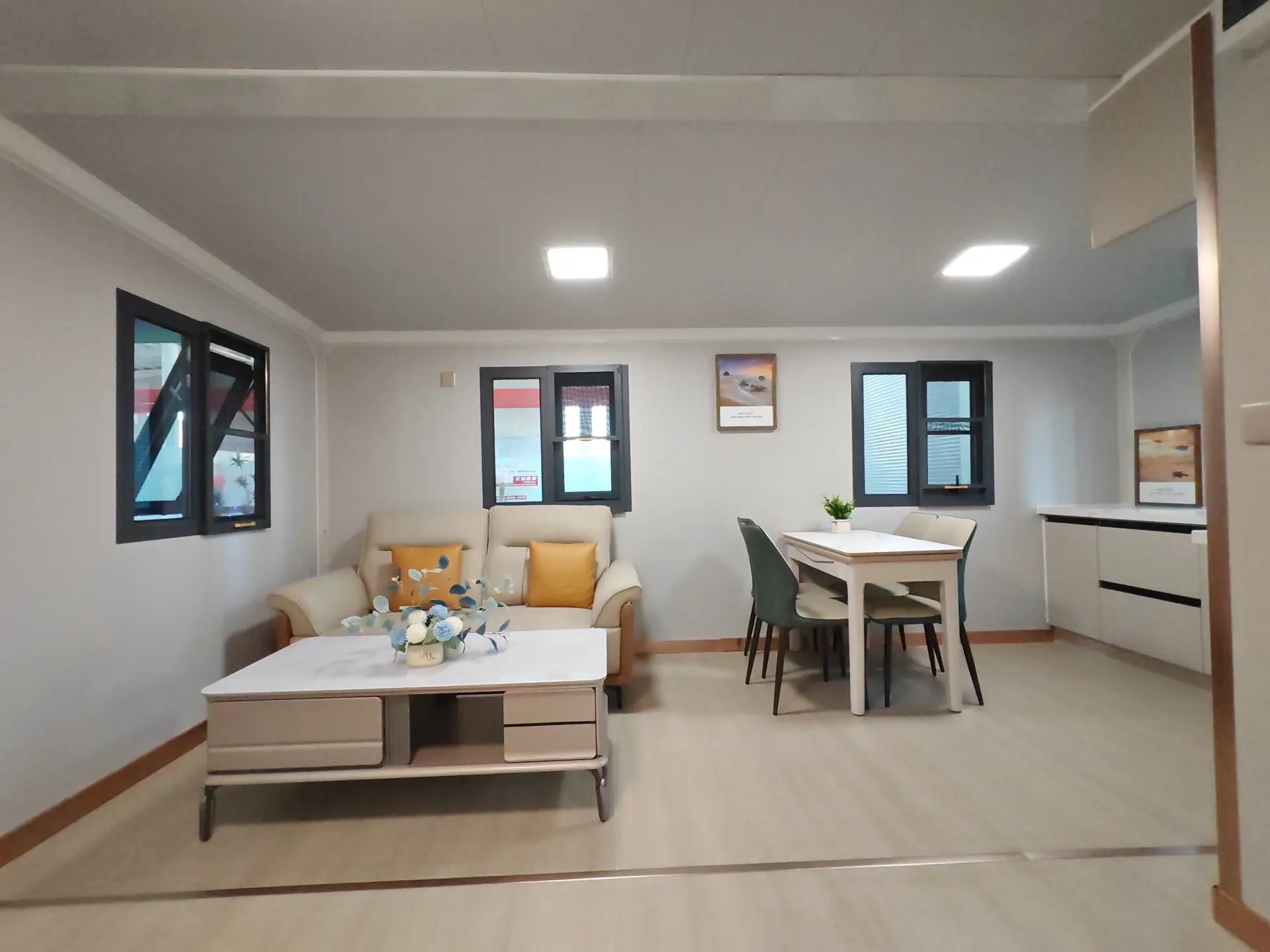
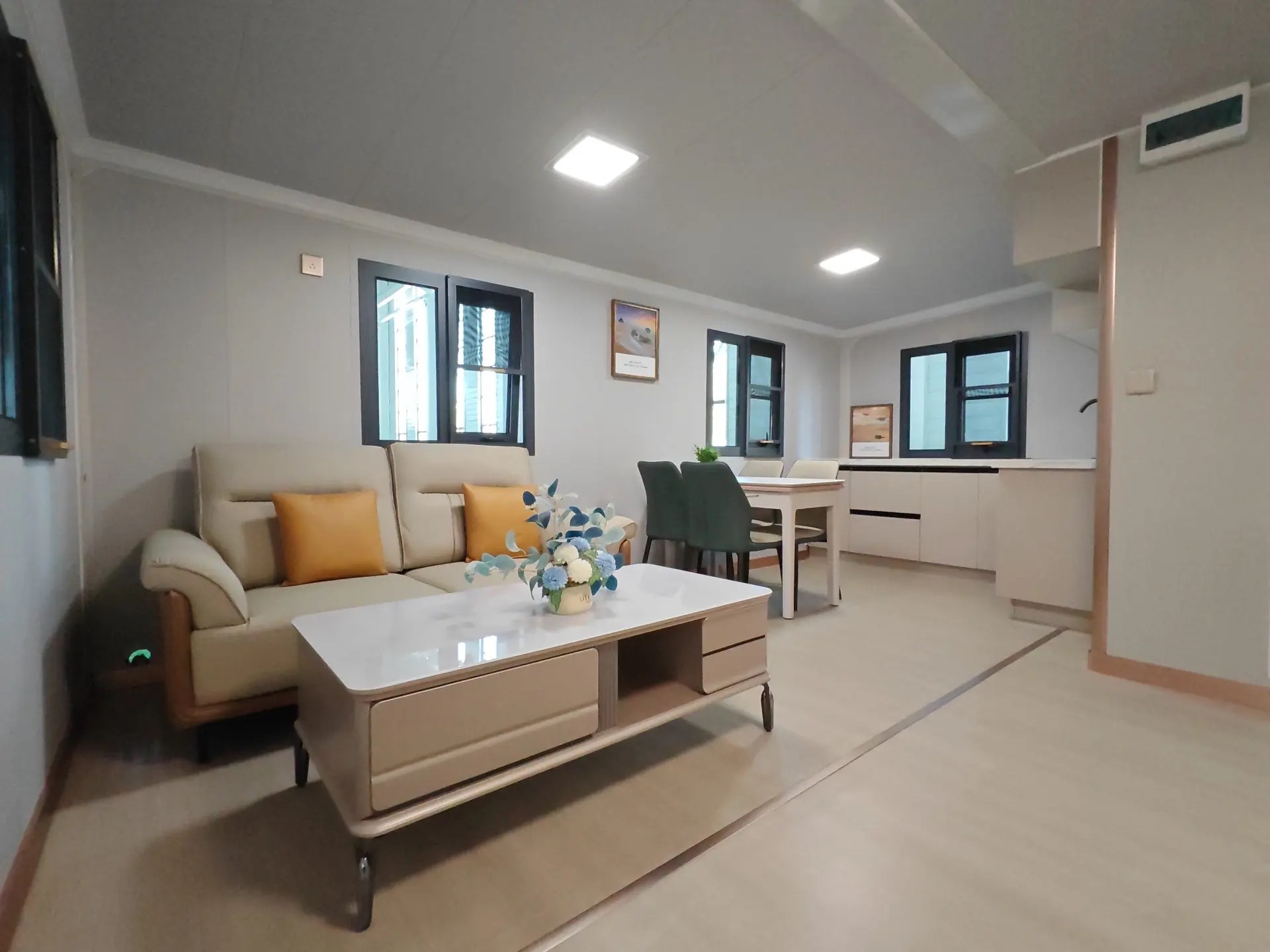
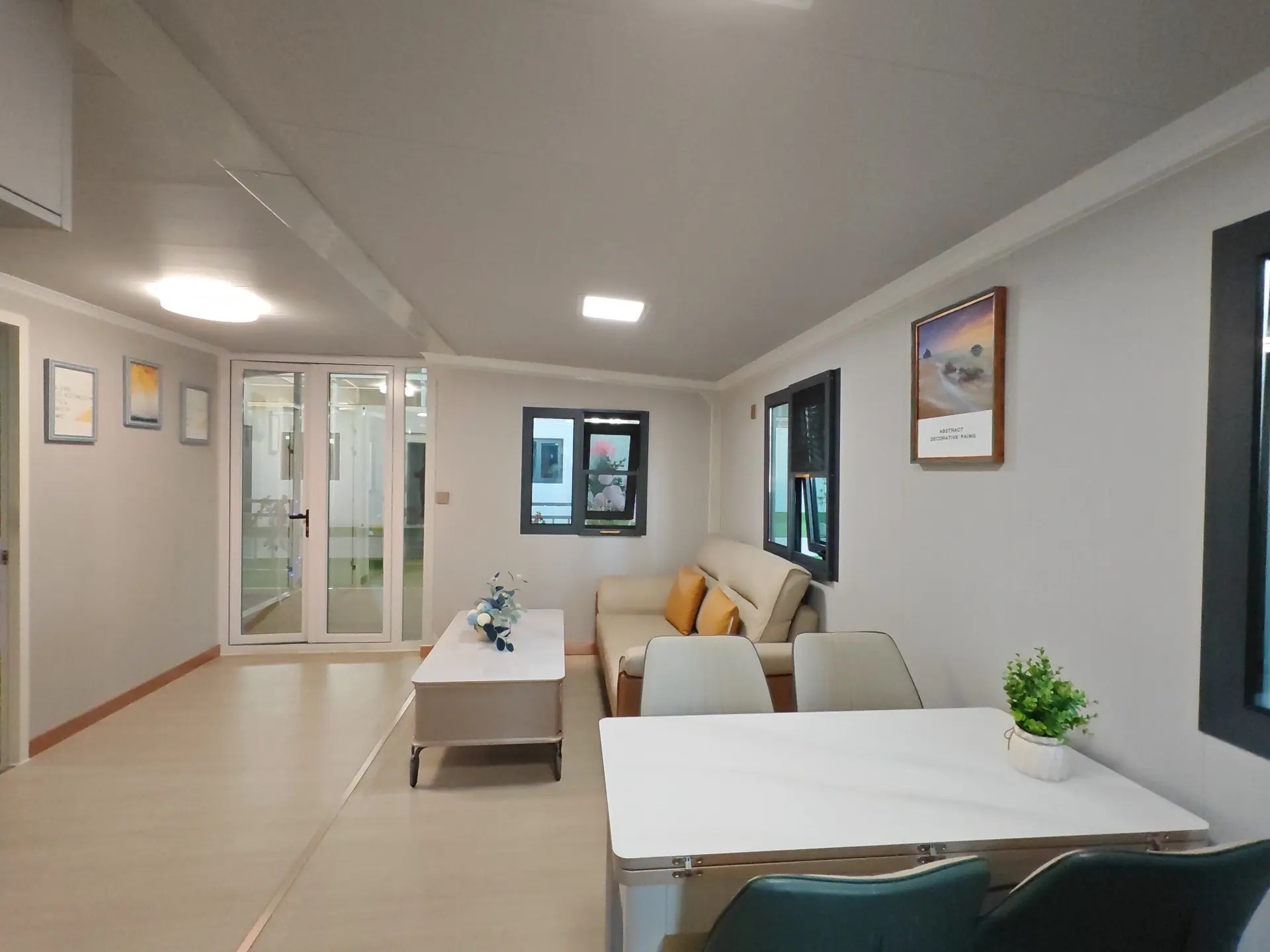
Design flexibility
Most models allow internal walls to be positioned according to project needs, enabling layouts for families, shared accommodation, tourism, or workforce housing.
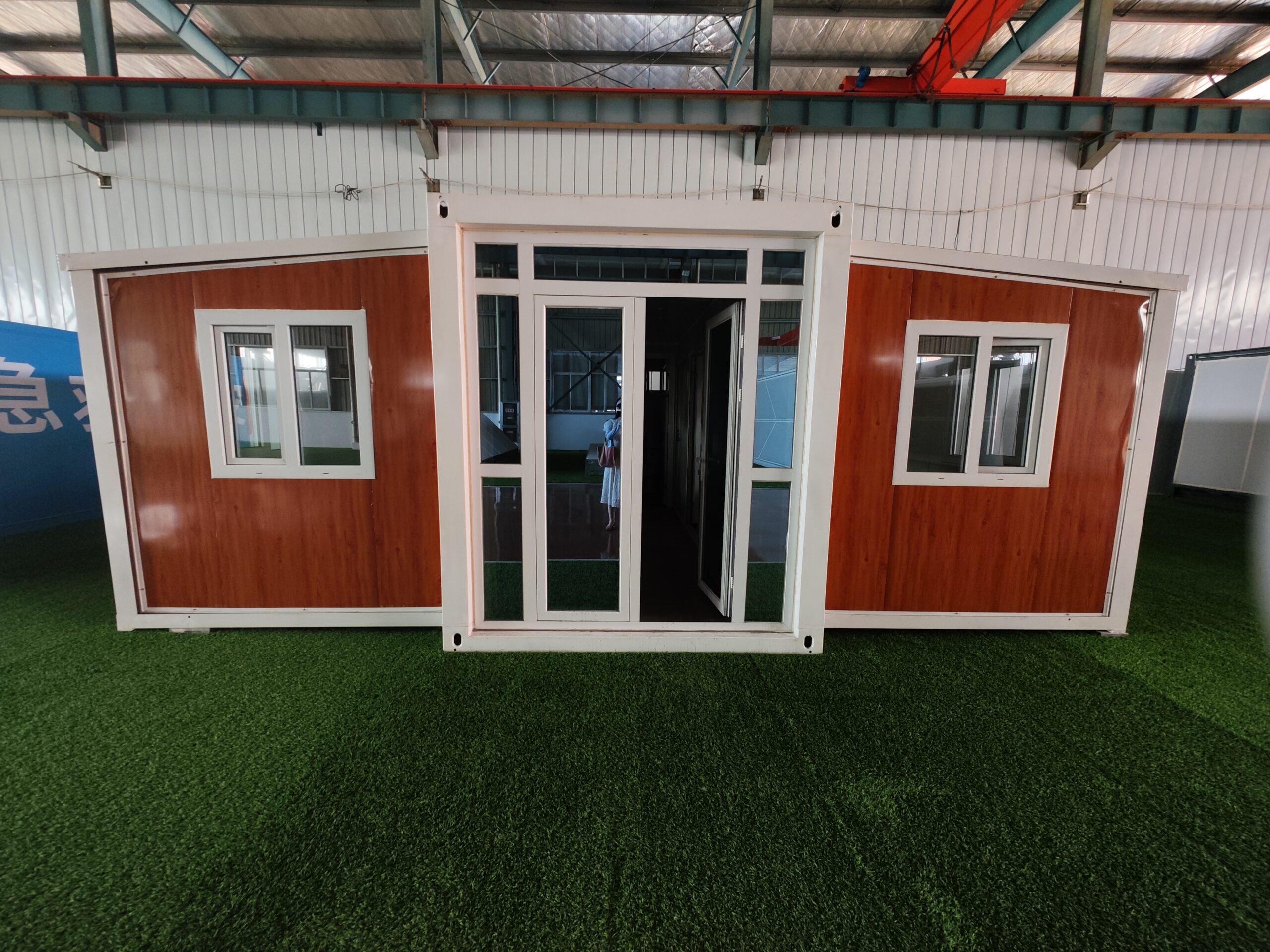
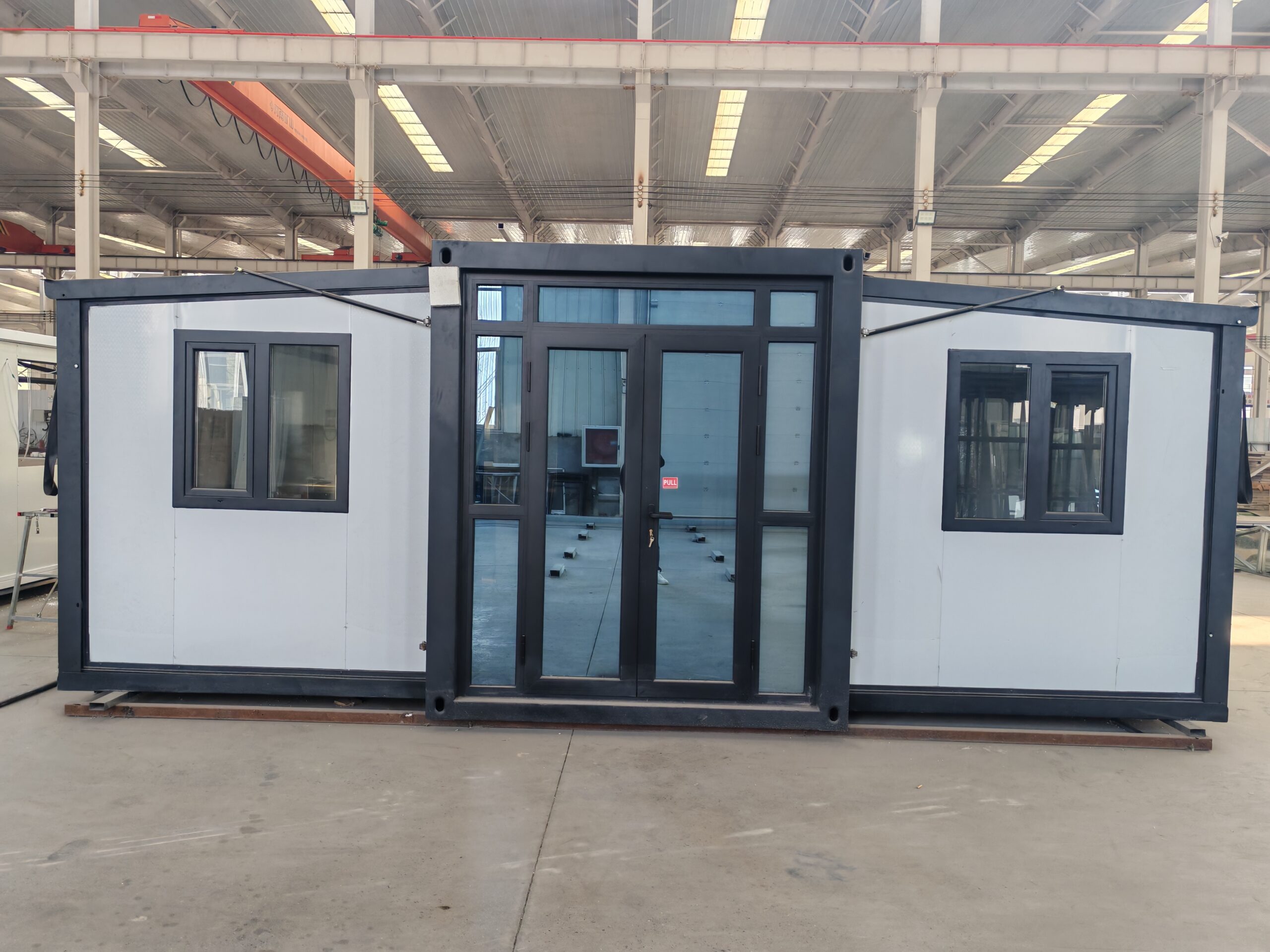
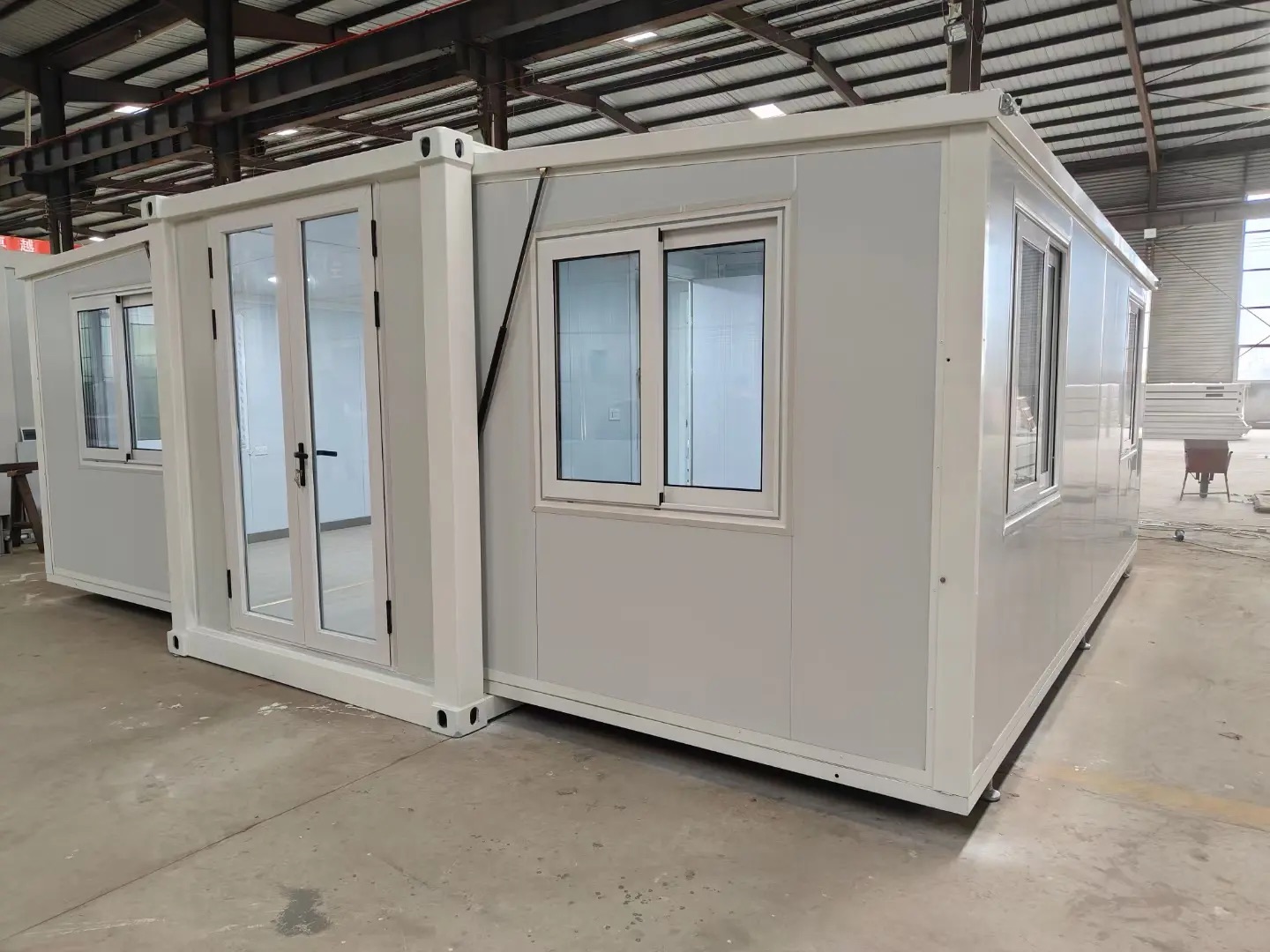
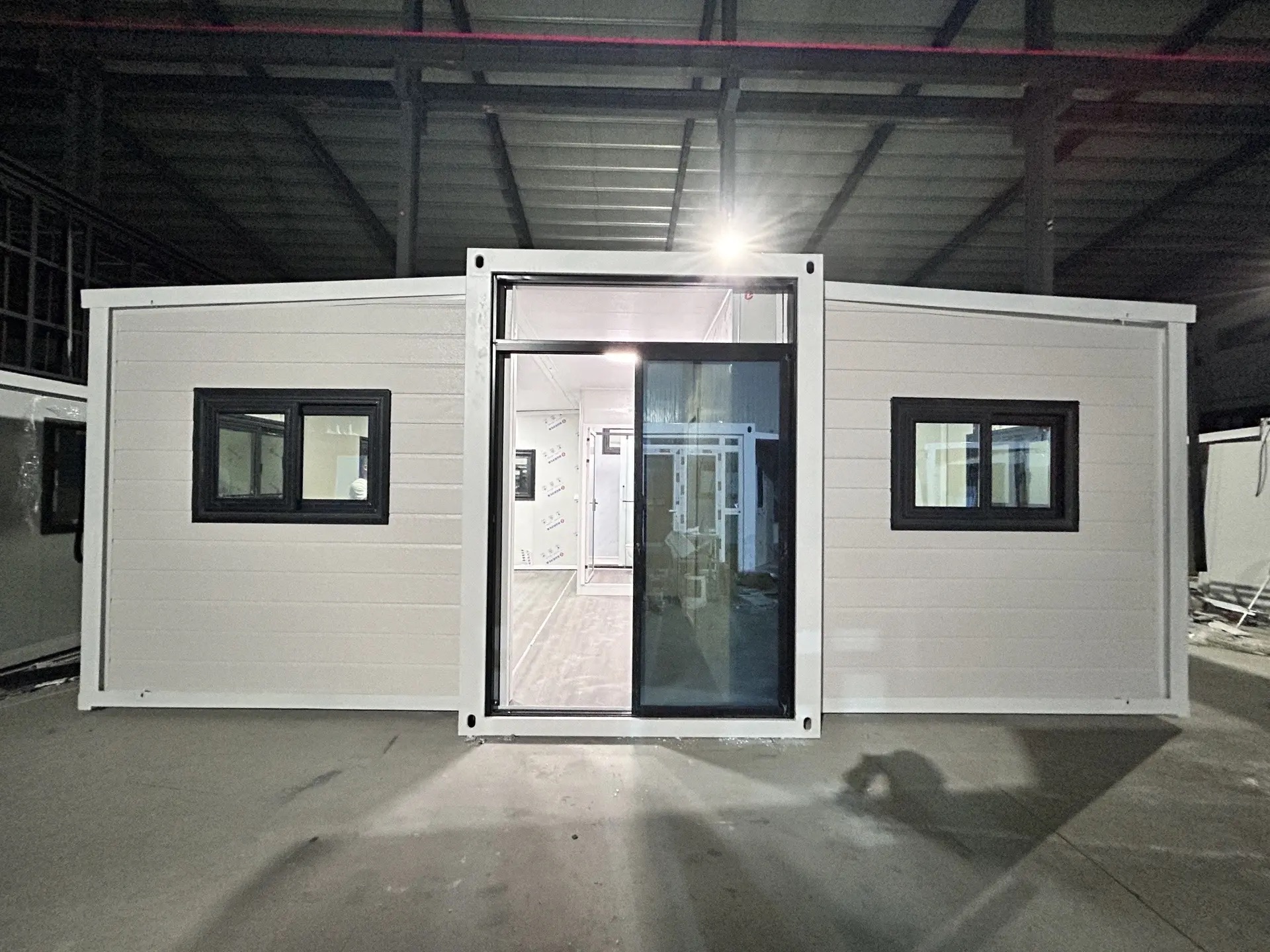
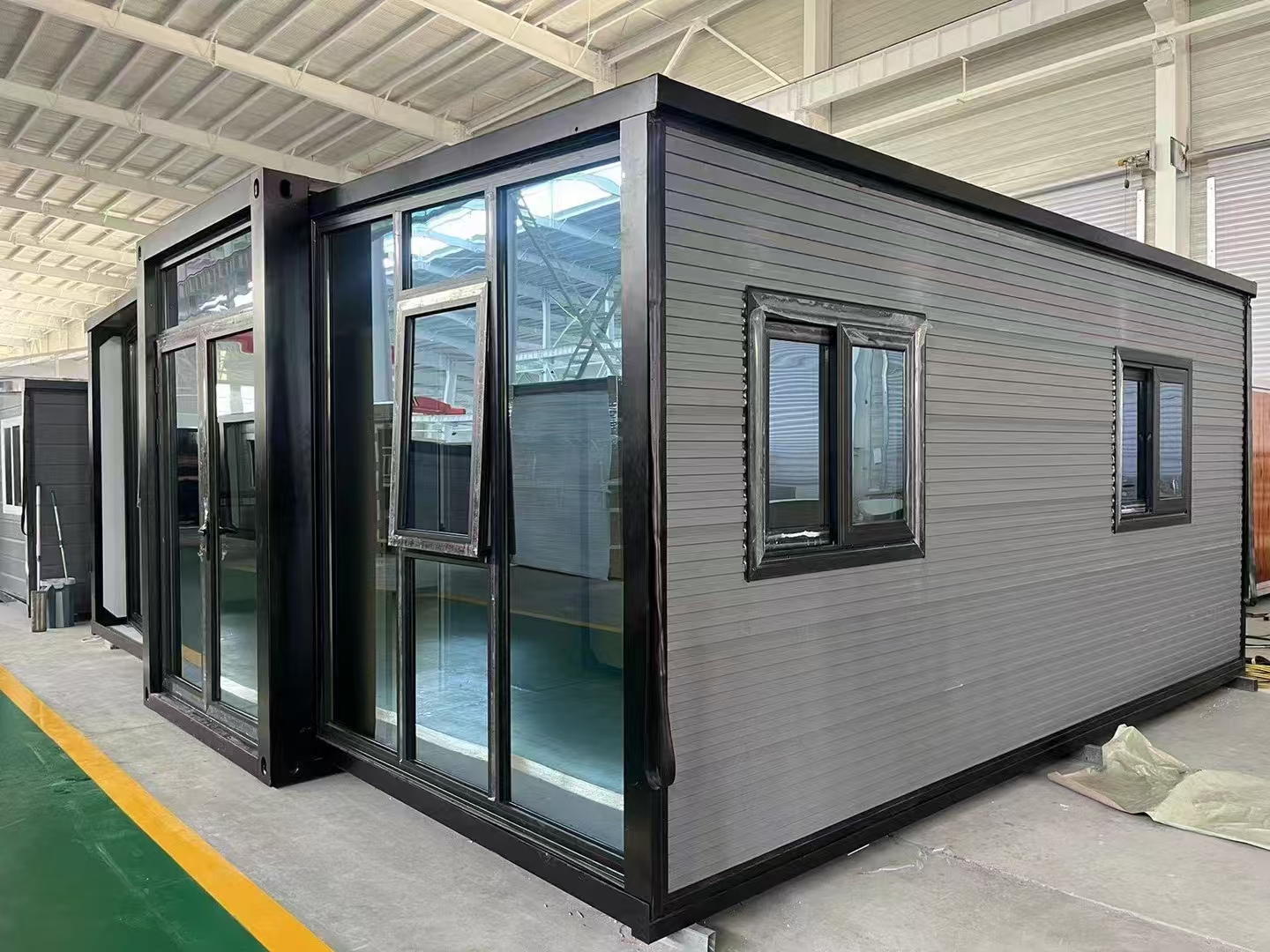
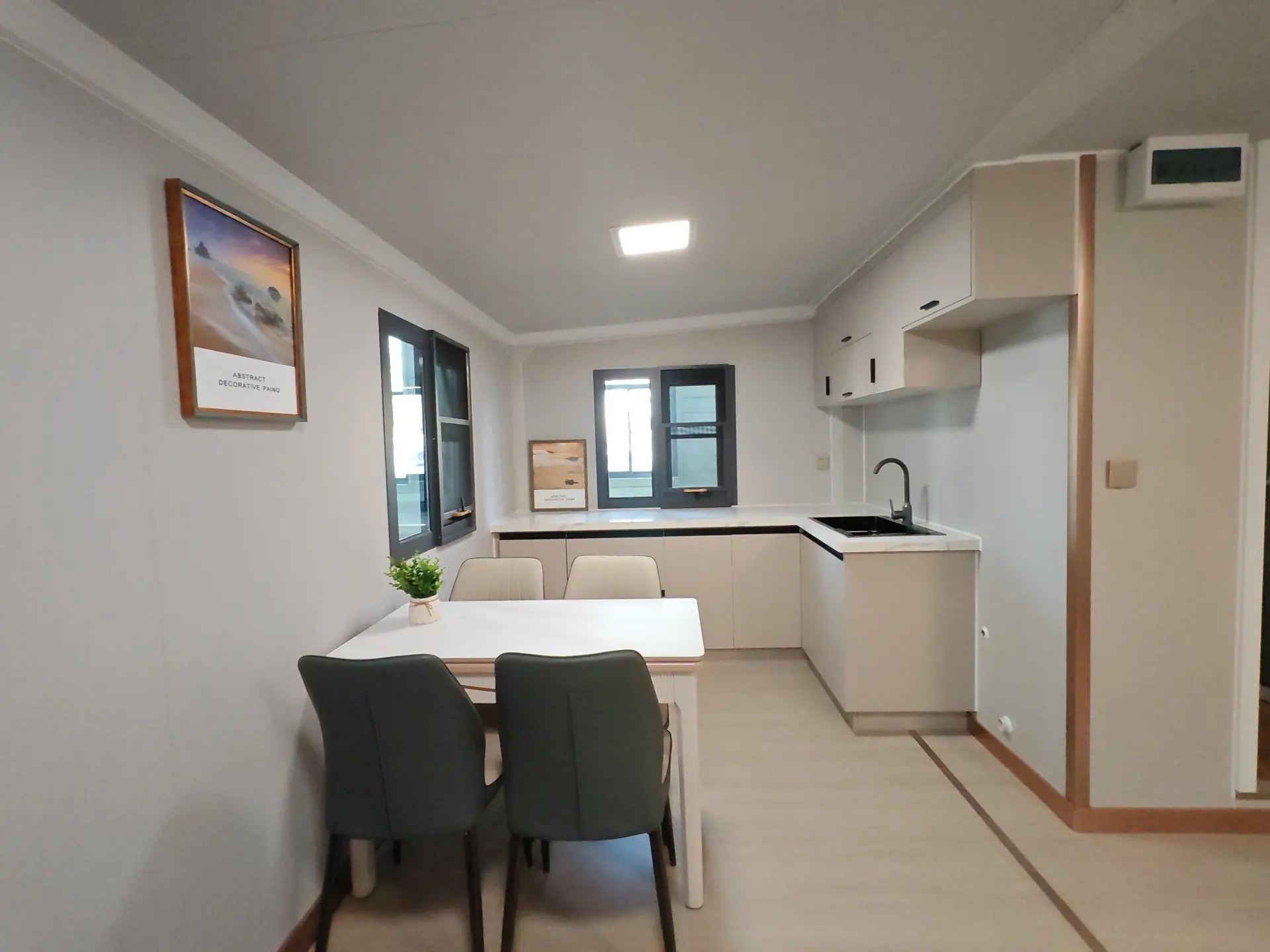
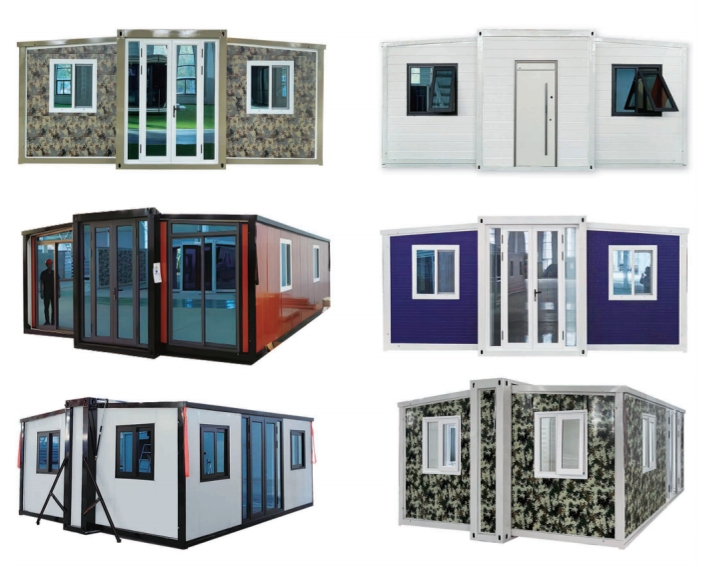
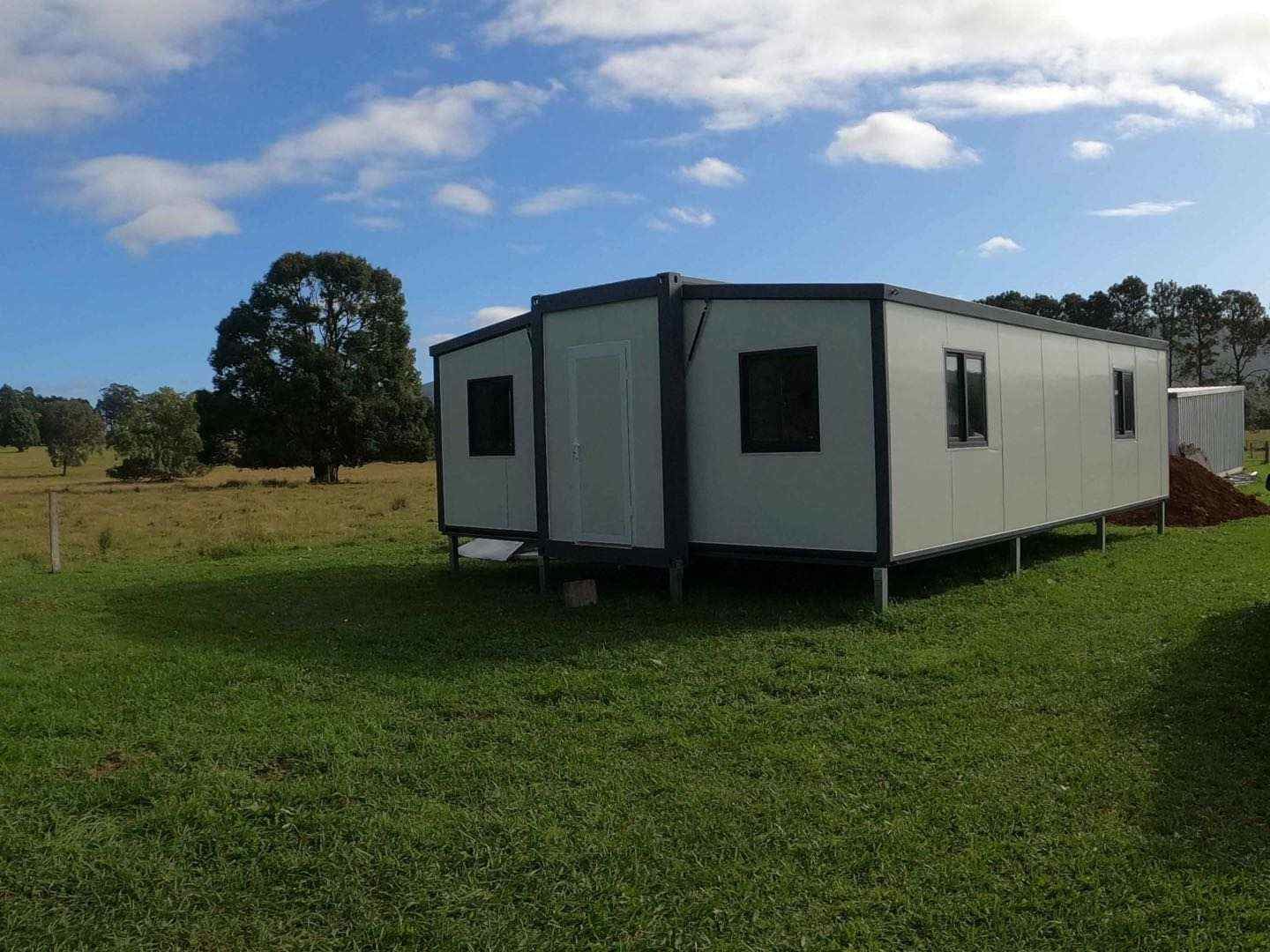
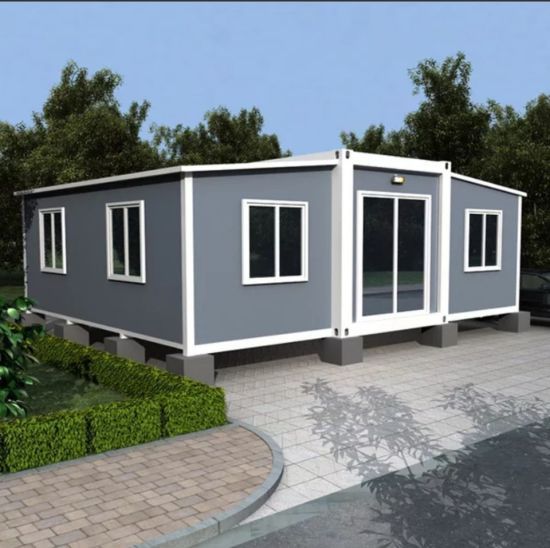
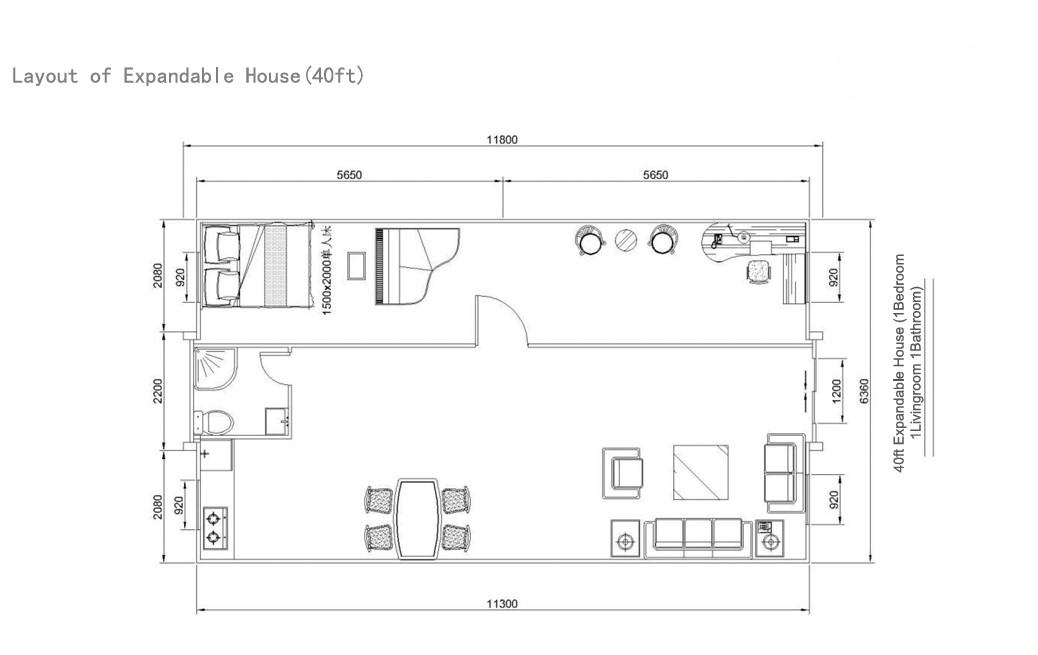
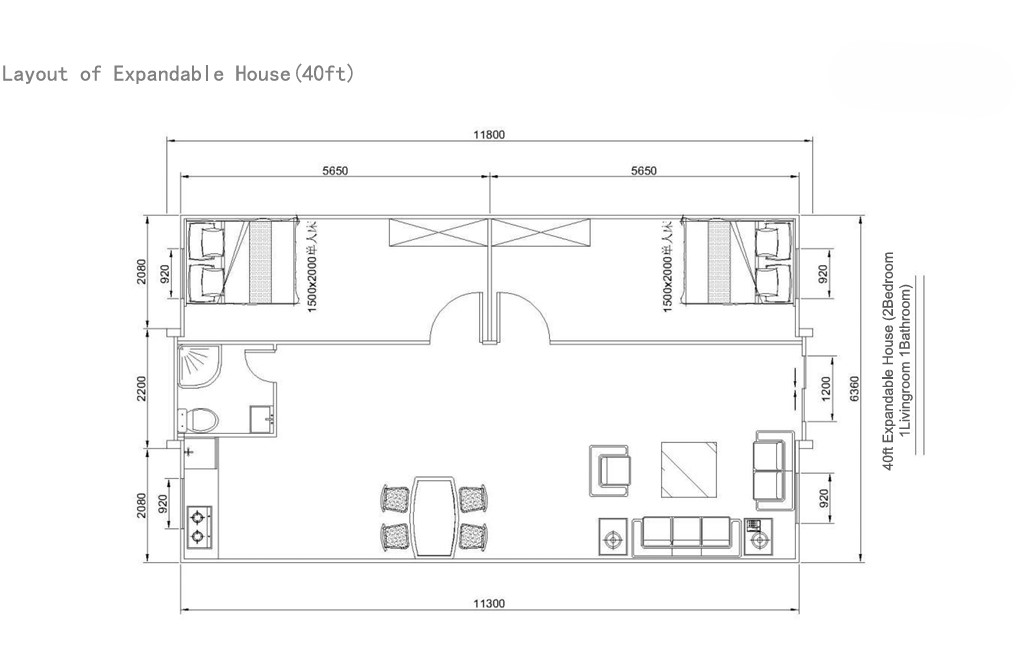
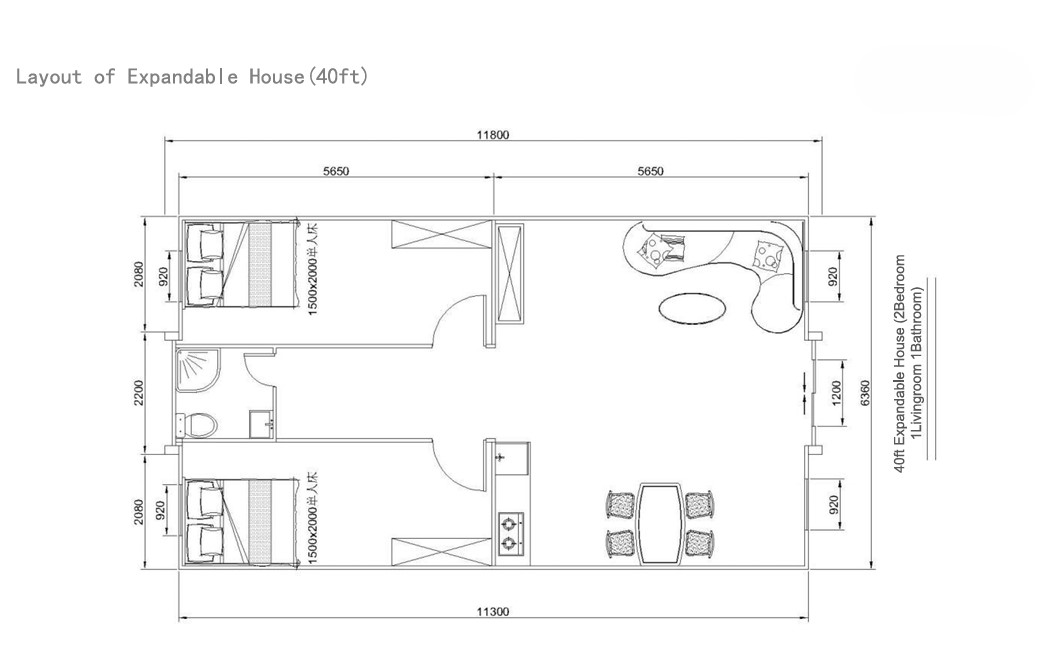
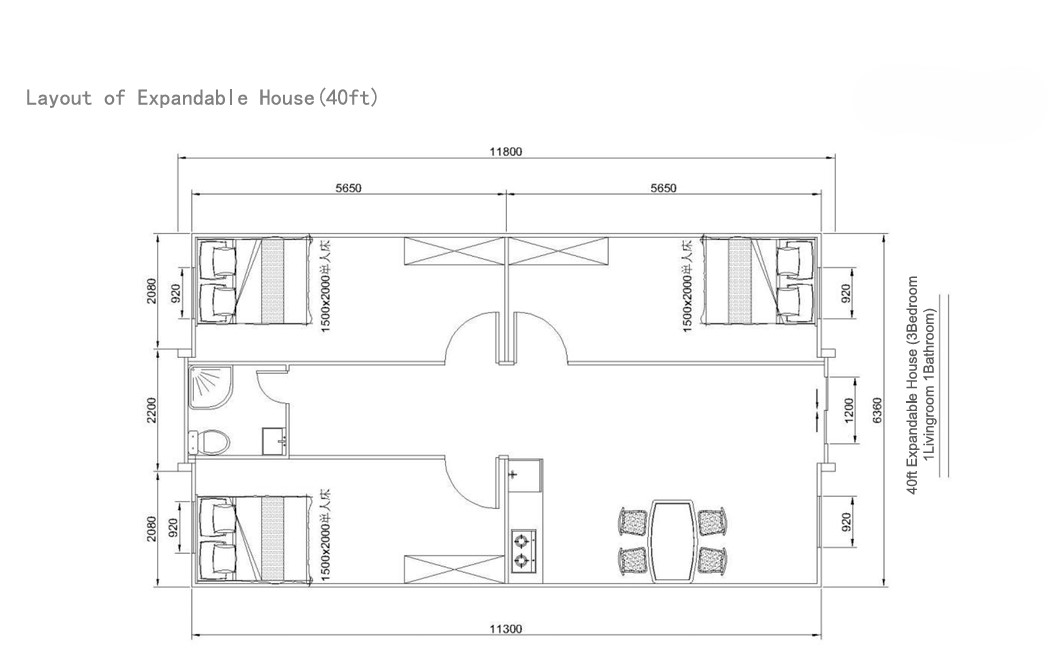
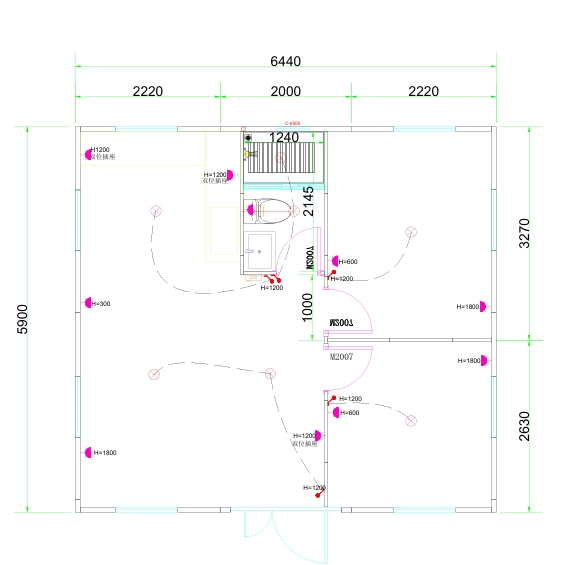
Available Sizes & Layout Concepts
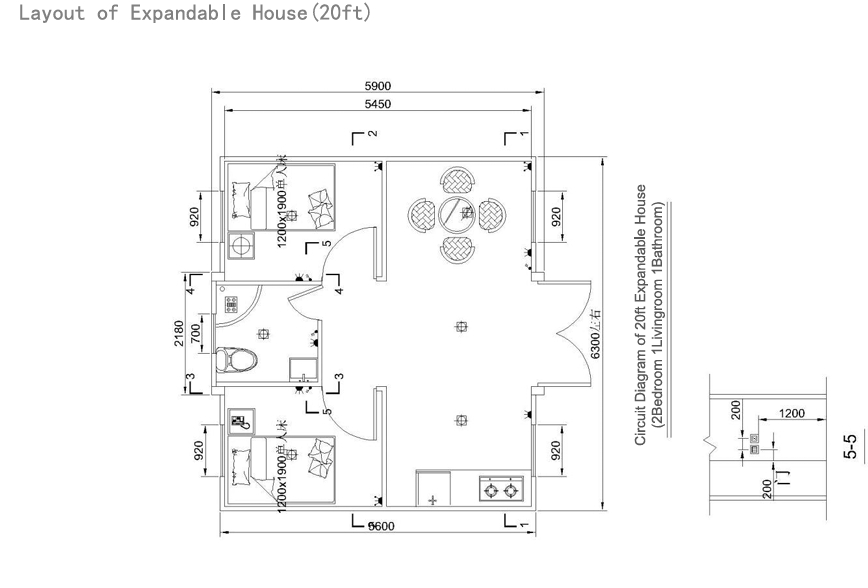
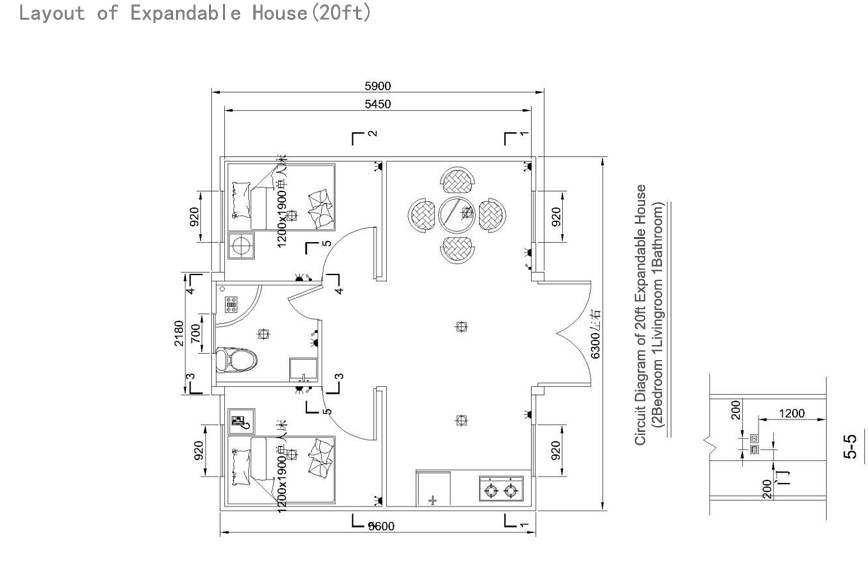
20ft expandable homes
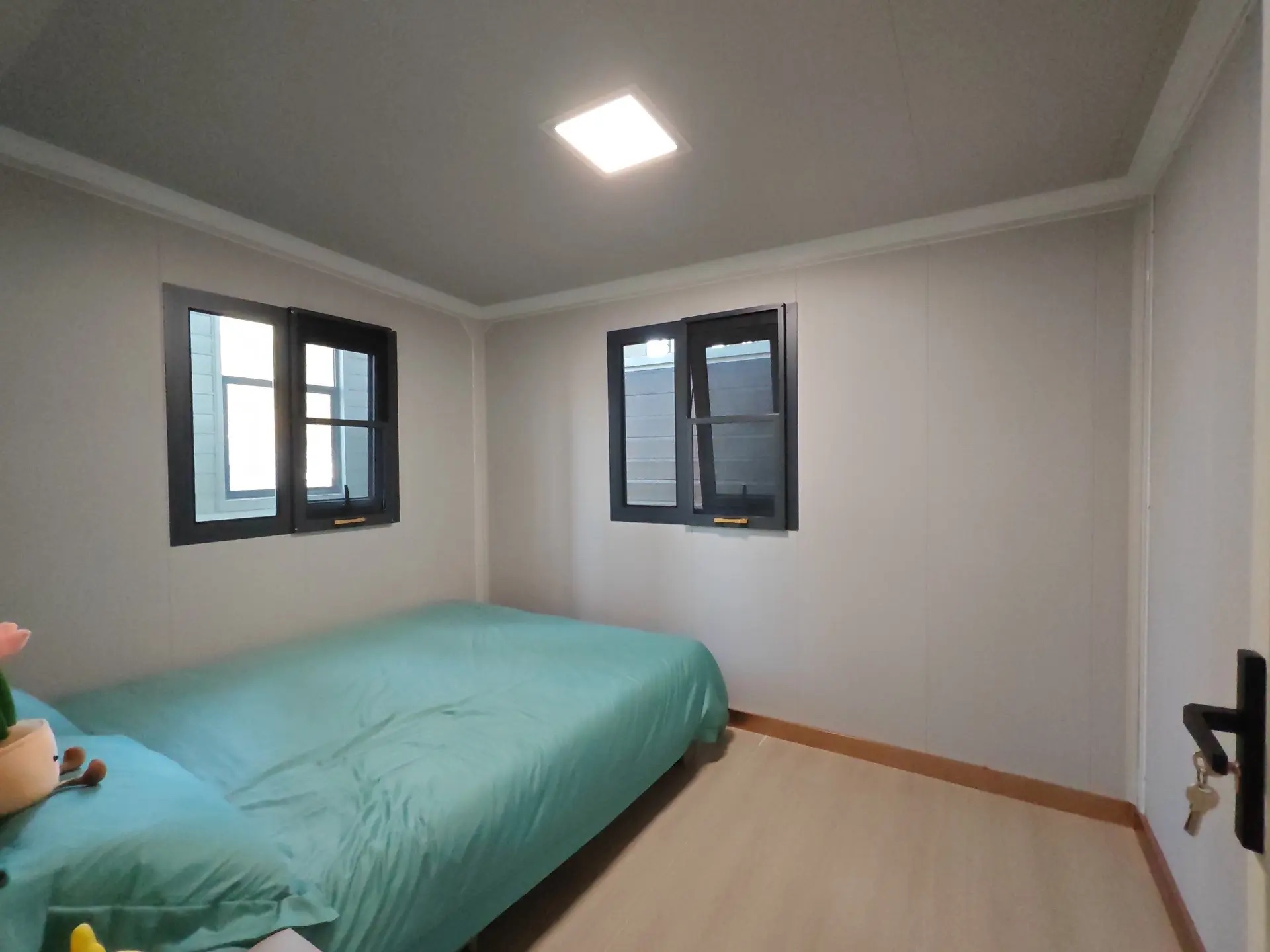
Typically suited to individuals, couples, or compact family living. Efficient design makes multi-room layouts achievable within a small footprint.
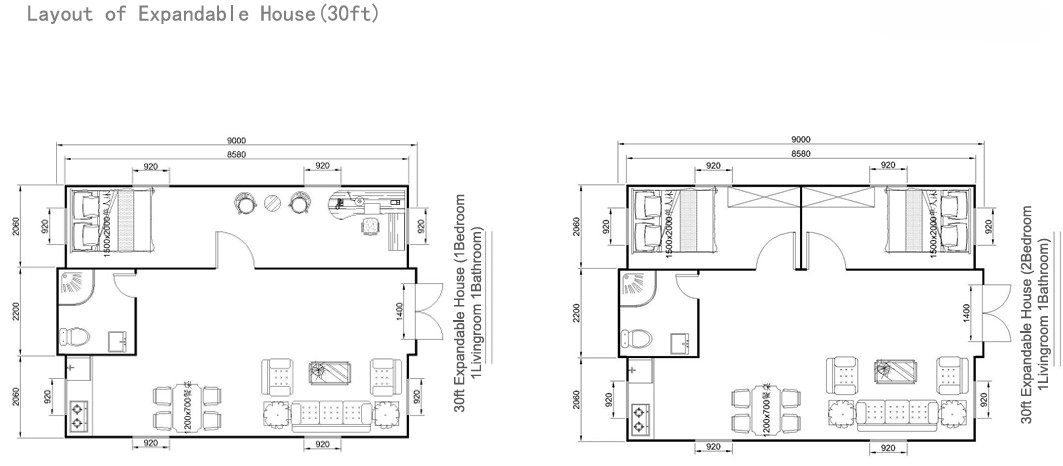
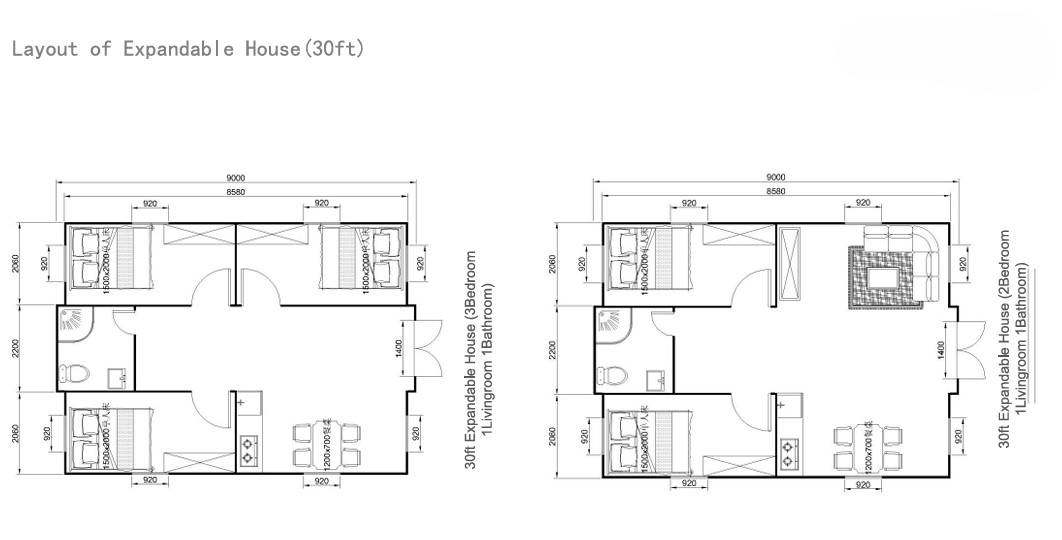
30ft expandable homes
A popular mid-range format offering larger living zones and additional bedroom capacity.
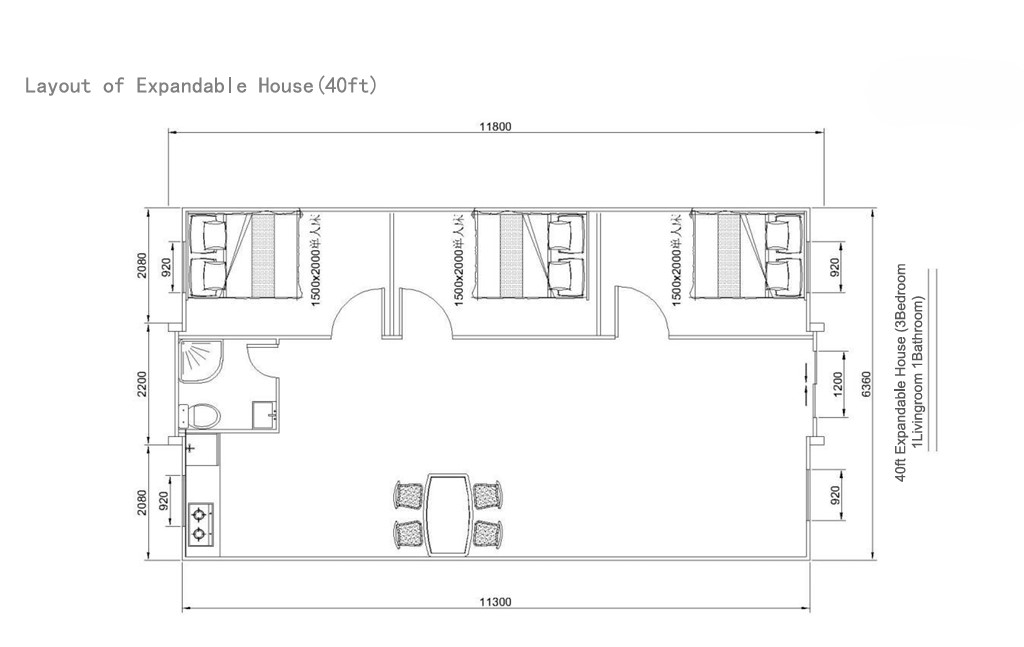
40ft expandable homes
Designed for broader family use, shared living, or open-plan configurations.
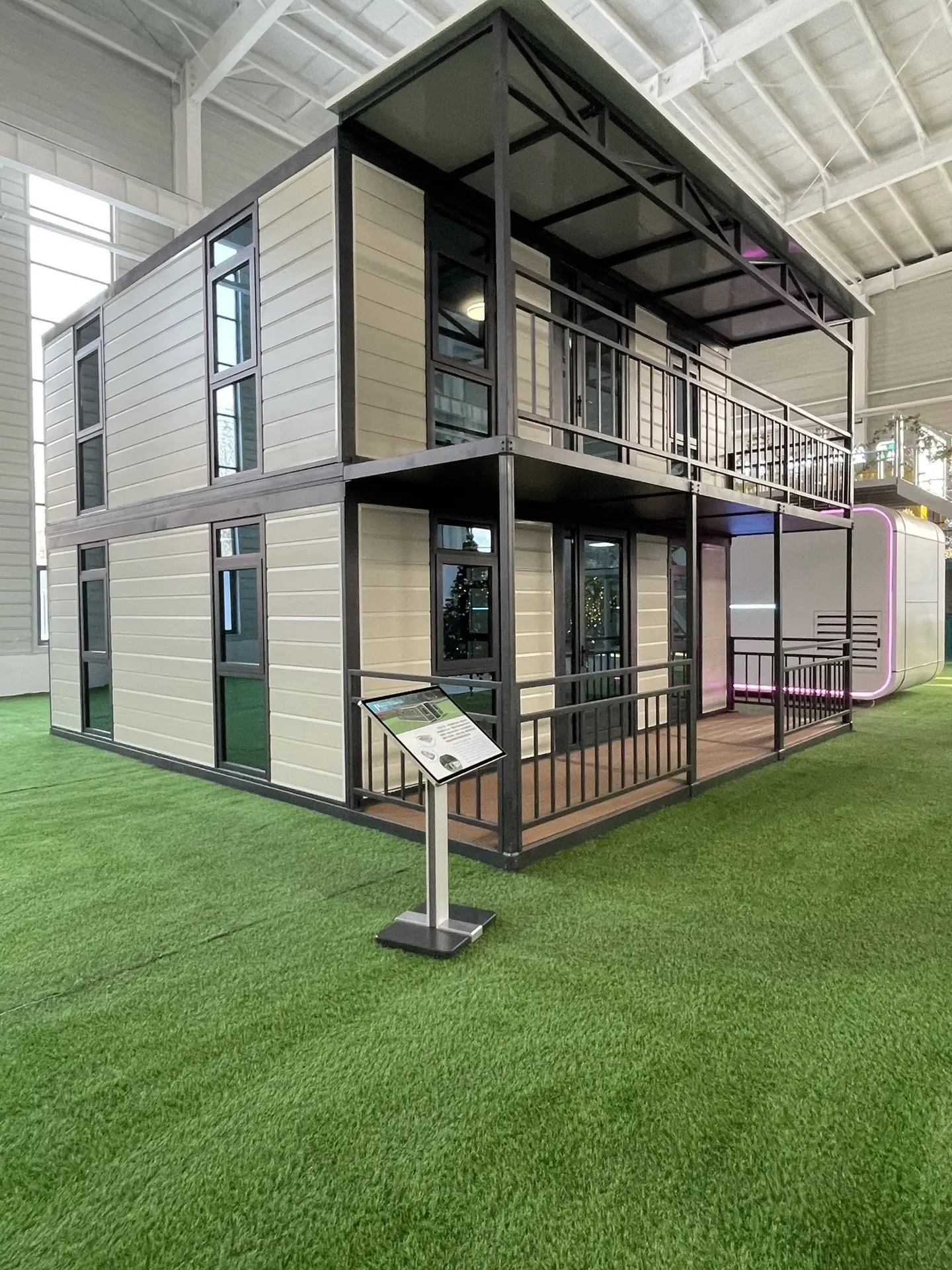
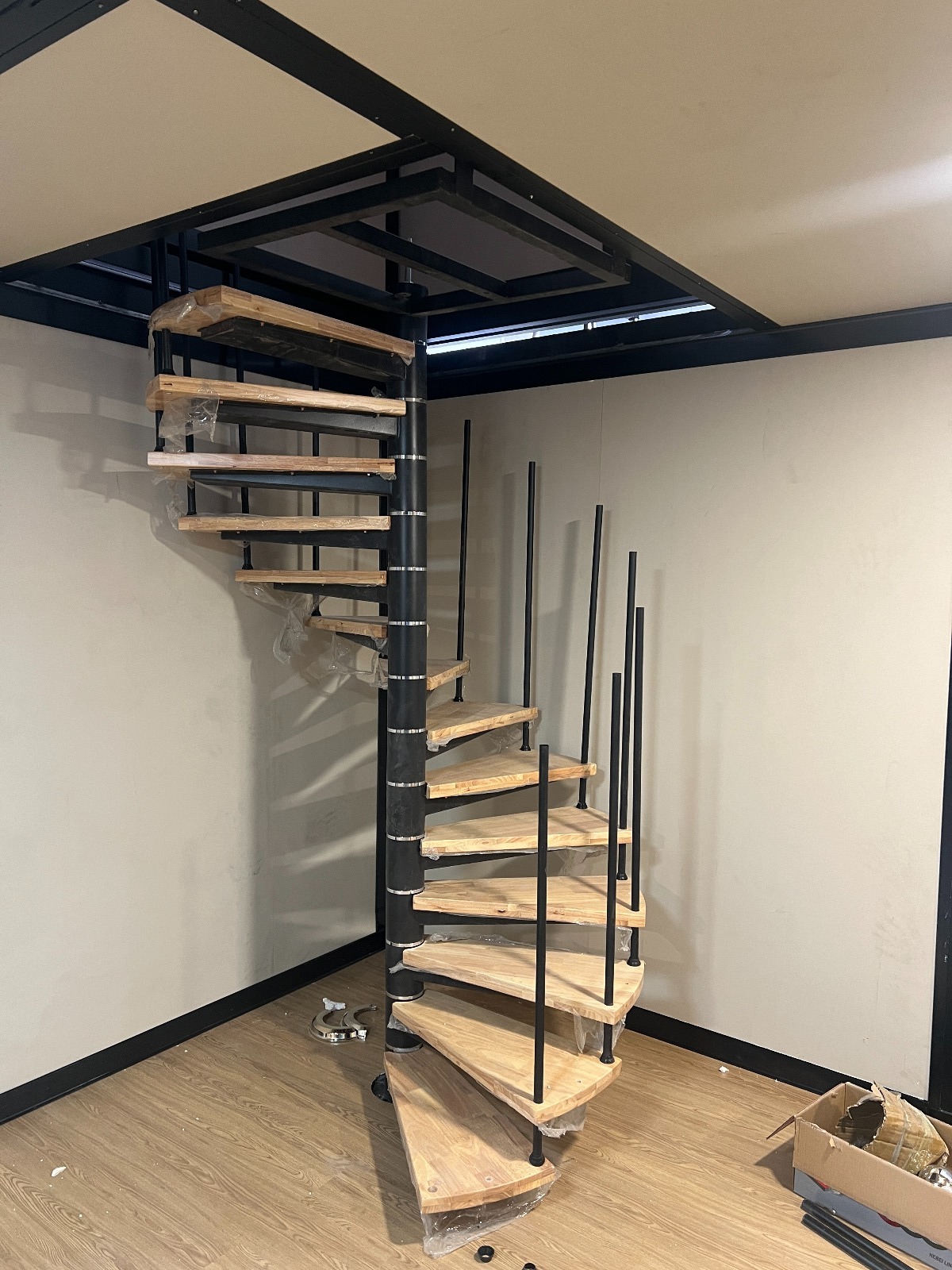
Two-storey expandable designs
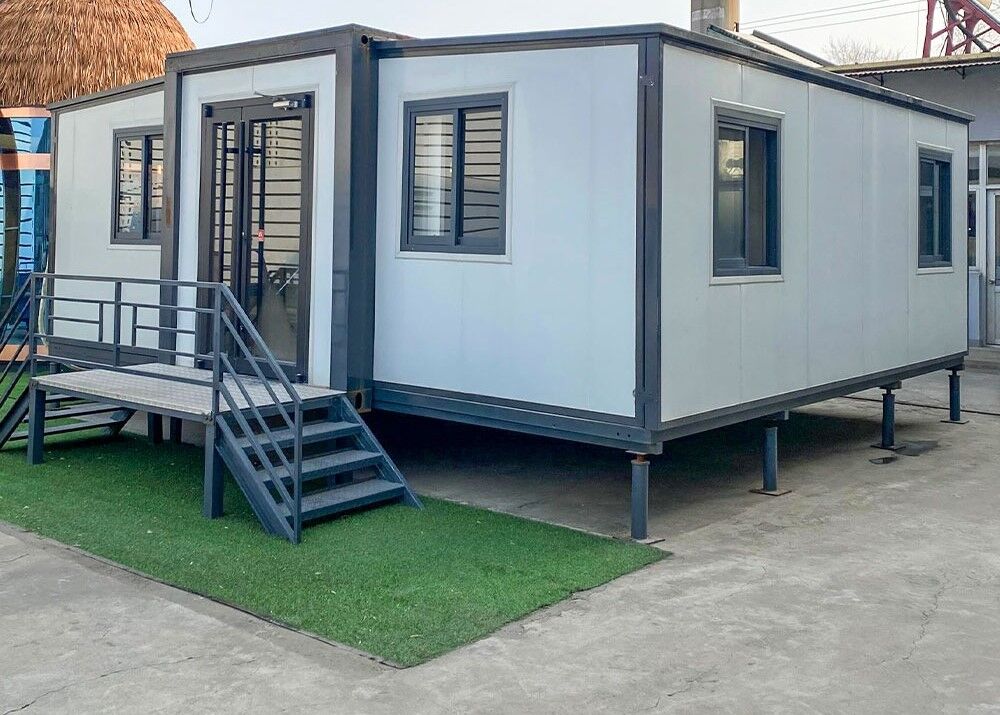
Where land area is limited, vertical layouts provide increased room count without expanding the footprint. Stair configurations may be internal or external depending on site requirements.
Built for Long-Term Durability
Structural assurance
Expandable container systems are engineered around reinforced steel frameworks intended for transportation stress as well as residential use.
Moisture and ventilation management
Integrated drainage paths, sealing methods, and airflow considerations help limit condensation and damp-related problems.
Coastal suitability
Many models include corrosion-resistant materials and optional upgrades for harsher marine environments.
Materials & Protective Treatments
Performance in demanding climates depends heavily on surface protection and metal treatment.
Common strategies include:
• Galvanised structural elements
• Zinc-rich primers
• Polyurethane or similar topcoats
• Stainless components in exposed areas
Layered protection significantly extends usable life and reduces maintenance frequency.
Engineering for Wind & Extreme Weather
Transportable housing must resist uplift, lateral forces, and fatigue in ways conventional buildings may not.
Anchoring options often include
• Concrete foundations with embedded connectors
• Ground screw systems
• Steel tie-downs
• Pile or pier supports
Correct anchoring improves resilience in cyclone, flood, and seismic regions.
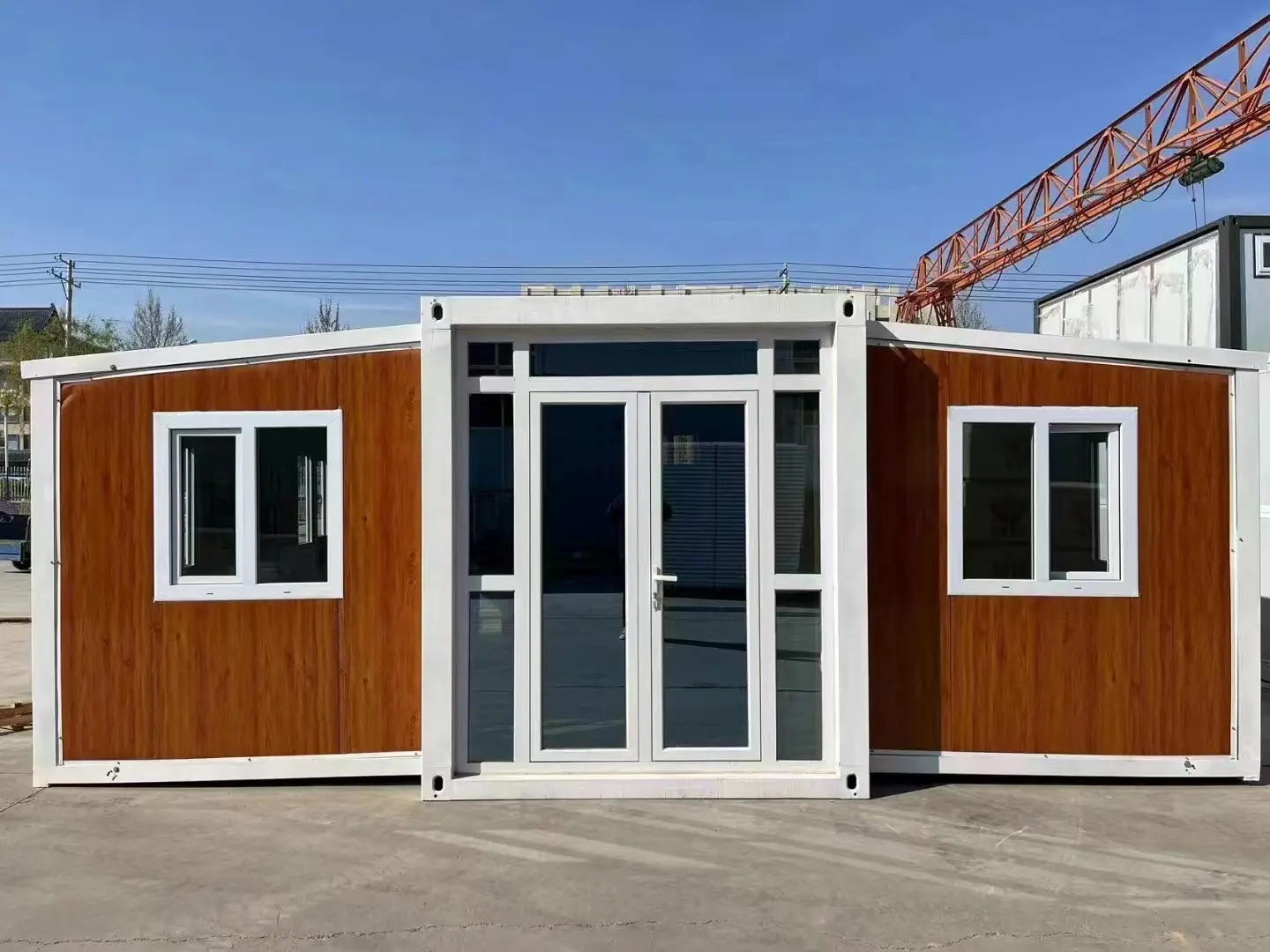
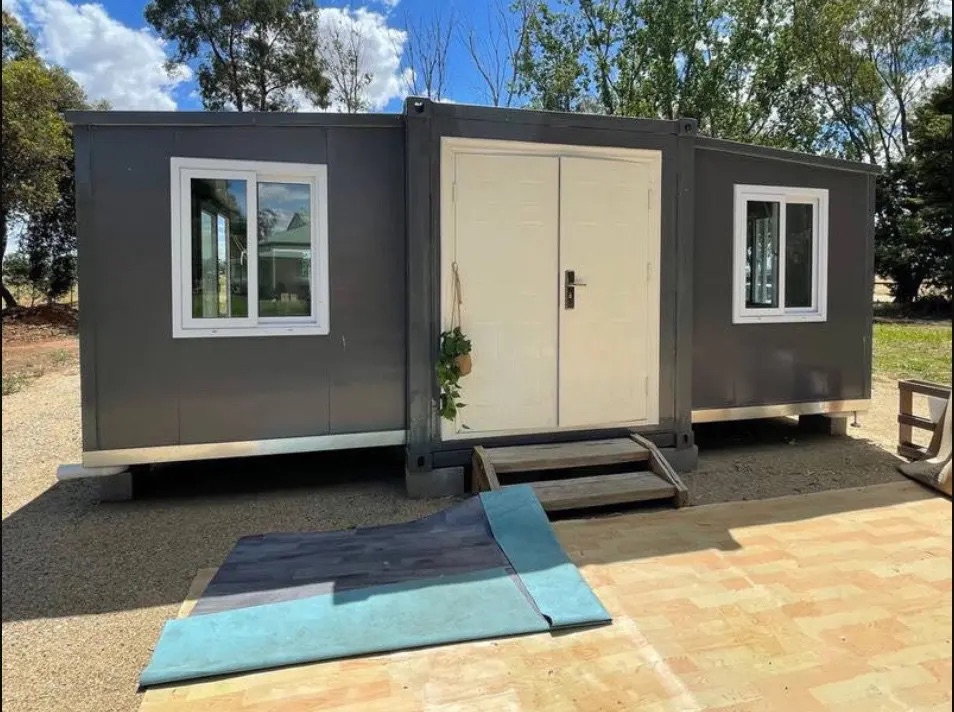
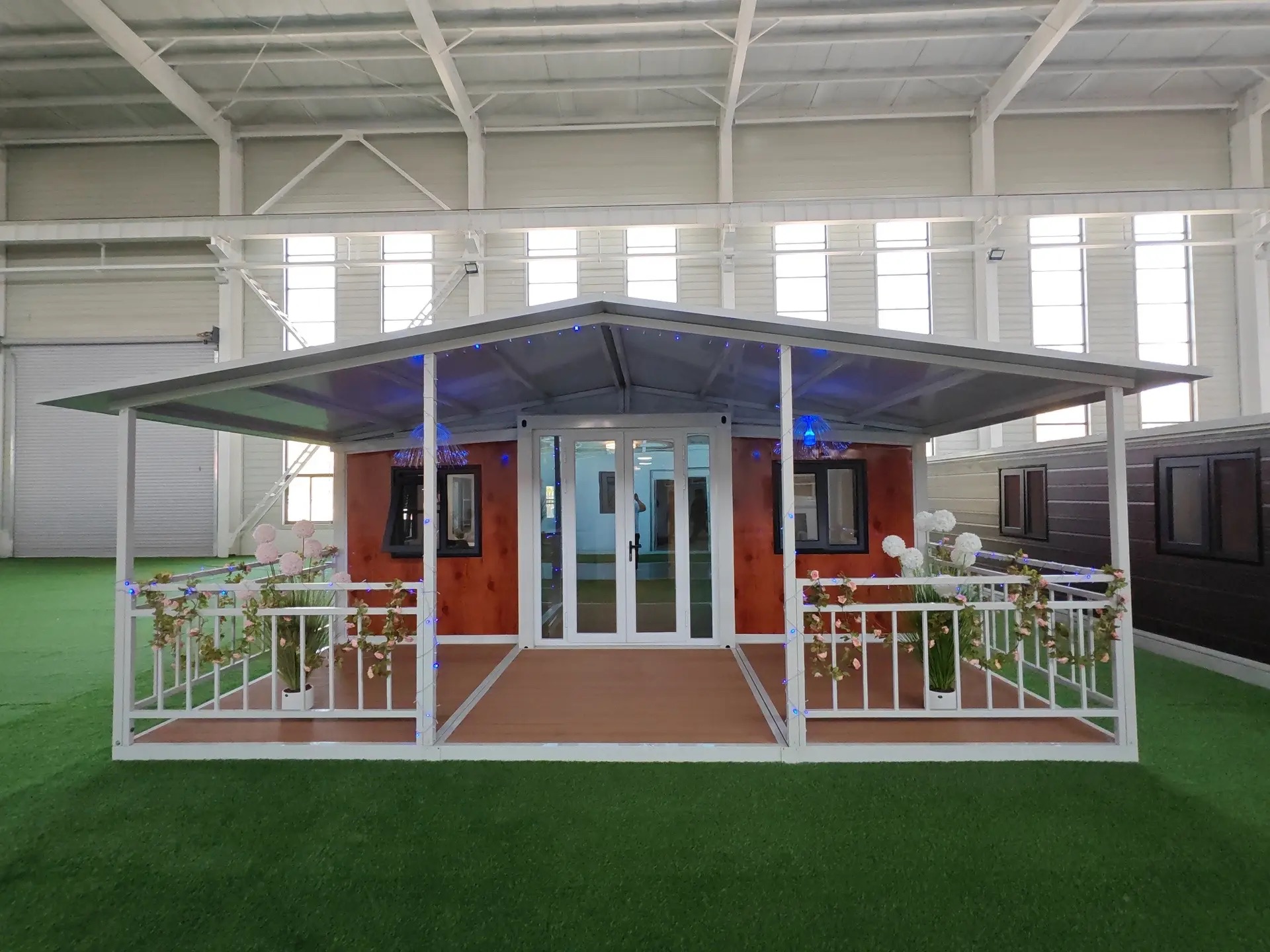
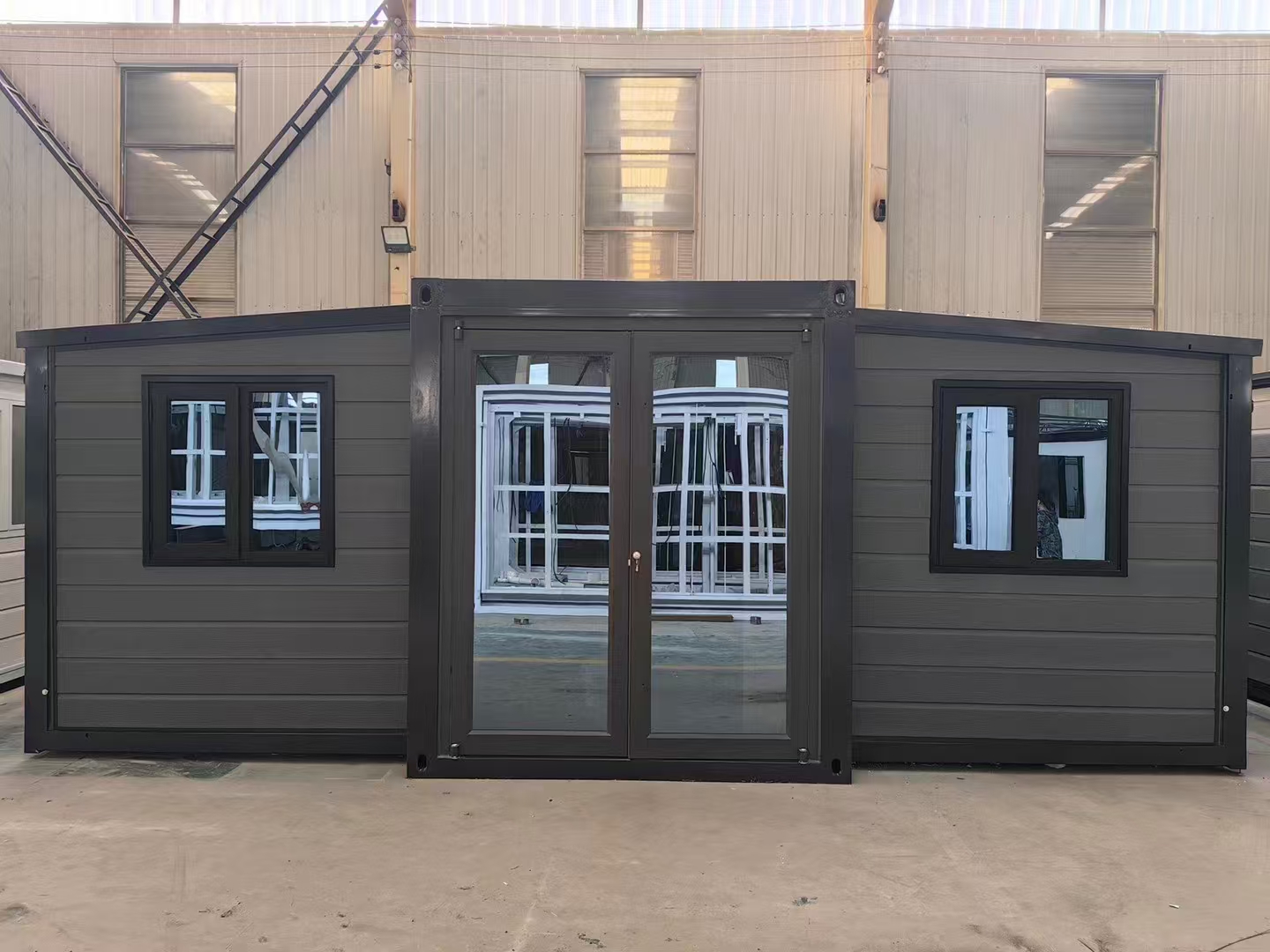
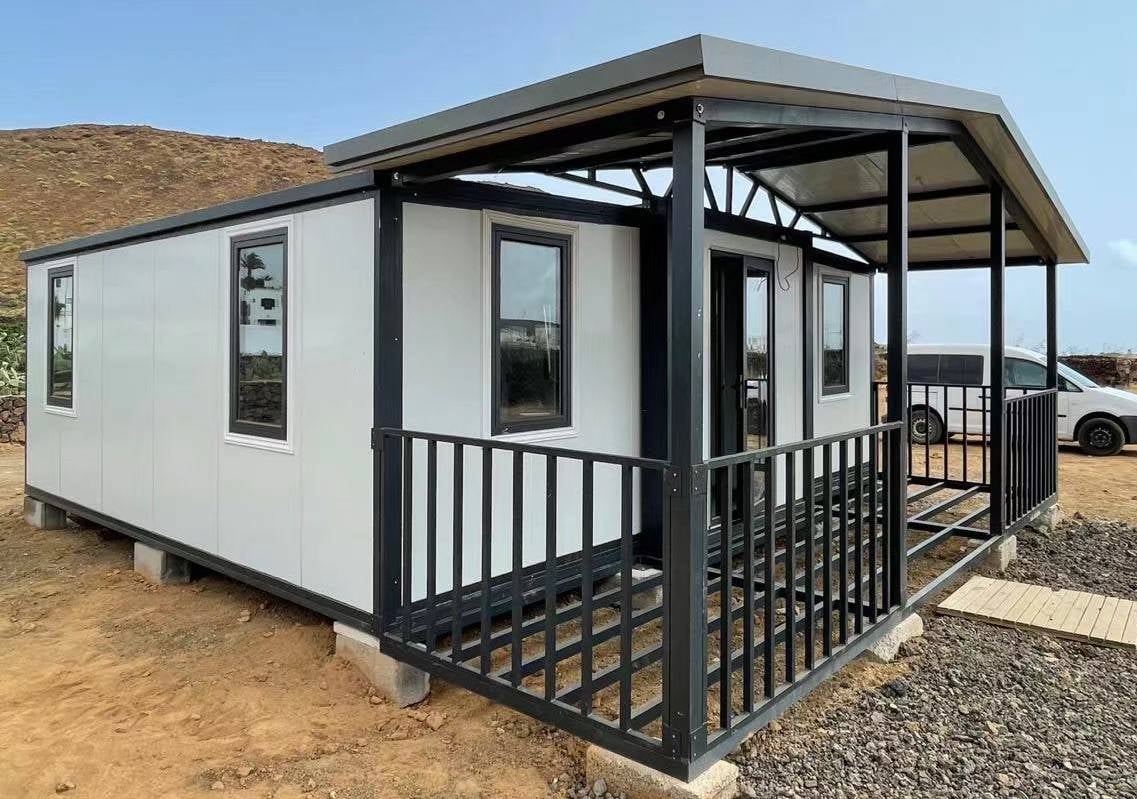
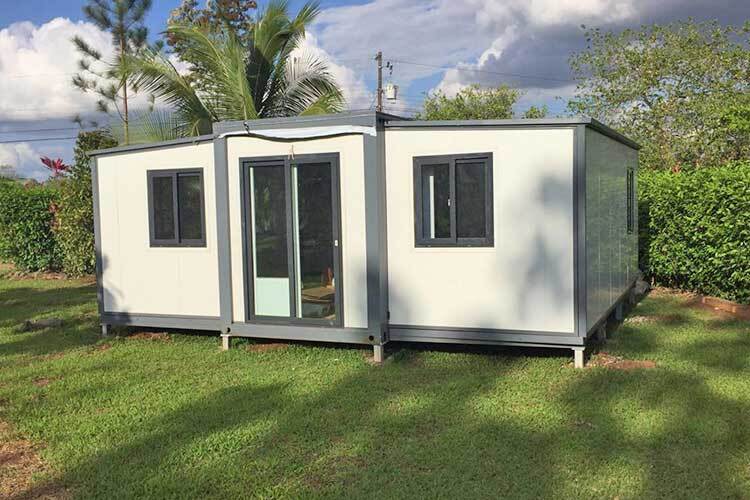
Exterior Appearance & Finish Options
While many expandable homes are recognised for a contemporary timber-look façade, alternative finishes are frequently available.
Buyers may select:
• Neutral modern palettes
• Industrial aesthetics
• Textured or matte surfaces
• Custom colour programmes
Bespoke finishes usually involve additional cost due to specialised coatings and production changes.
Where Expandable Housing Performs Best
Expandable container homes are particularly effective in situations requiring rapid delivery, cost control, or environmental resilience.
They are widely used for:
• Primary residences
• Holiday accommodation
• Rental investments
• Eco-living developments
• Workforce housing
• Remote community projects
Global Adoption & Market Growth
Demand for expandable housing is increasing in regions facing climate exposure, population pressure, or limited construction infrastructure.
Pacific nations
Rapid deployment, transport efficiency, and storm resilience make modular housing attractive for island environments.
India
Urban density and affordability challenges are driving interest in repeatable housing formats.
Africa
Both remote and metropolitan areas benefit from speed, durability, and the potential for off-grid utilities.
Central & South America
Tourism growth and disaster resilience planning are encouraging modular alternatives.
Expandable vs Traditional Construction
The decision often comes down to:
• build time
• cost certainty
• environmental exposure
• access to skilled labour
• future relocation or expansion potential
Factory production allows higher consistency while reducing on-site risk.
The Bigger Shift in Housing
Expandable container homes represent more than a trend toward modularity. They are part of a broader movement toward housing that can be transported, installed quickly, and engineered for diverse climates.
As infrastructure pressure increases globally, adaptable building systems are likely to become a standard component of residential and commercial planning.
If homes can now be manufactured with the same precision as vehicles or machinery, the future of construction may be less about building slowly on site — and more about deploying performance-ready structures where they are needed most.